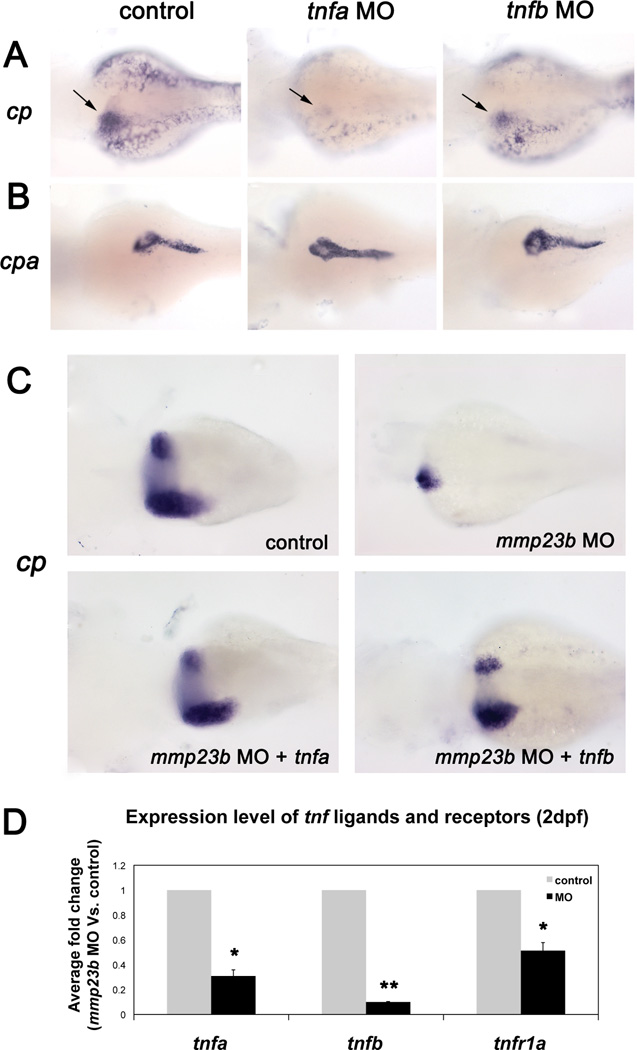
Figure 4. tnfa and tnfb function downstream of mmp23b.
(A) WISH using a cp probe at 3dpf. Control embryo and tnfa/tnfb morphant embryos (tnfa, 85.2%, n=27; tnfb, 68.2%, n=22). Note dramatically reduced expression of cp (black arrow). (B) WISH using a cpa probe. Note the similar expression pattern of cpa in all embryos (tnfa, 95.8%, n=24; tnfb, 95% n=20). (C) WISH using a cp probe at 4dpf. Control embryo and mmp23b morphant (100%, n=18). Note the severely reduced liver size (arrow). Mmp23b morphant injected with tnfa/tnfb mRNA at 1-cell stage (I, 63.4%, n=33; J, 41.4% n=29). Note the restoration of liver development. (D) Fold changes of tnf ligands and receptor in control and mmp23b morphant embryos at 2 dpf. The expression levels of each marker were measured by quantitative RT-PCR and fold changes were calculated by comparing morphants expression level to that of the control embryos. β-actin serves as the reference gene. Error bar represents the standard deviation. *P<0.005, **P<0.0005.