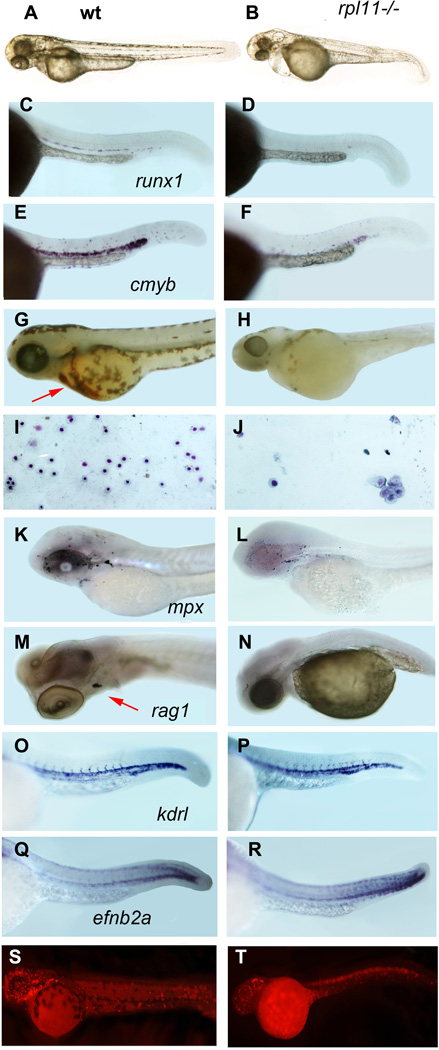
Fig 2.
The rpl11 mutant has developmental and haematopoietic defects. (A, B) At 48 hpf, rpl11 mutants had smaller heads and eyes, underdeveloped liver/gut and occasionally pericardial oedema. (C–F) The number of HSCs marked by expression of runx1 (C,D) and cmyb (E,F) is reduced in the mutant, in situ hybridization, 30 hpf, 30 embryos per group (G,H) Only few red blood cells remained in the mutant after day 3·5. O-dianizidine staining, 84 hpf, 30 embryos per group. Arrow points to erythrocytes in the wild-type embryo (I,J) Some erythroid cells from the blood of a mutant embryo are macrocytic. Blood smears were prepared from individual embryos; the results are representative of 6–10 embryos. Giemsa stain. (K,L) The number of granulocytes in the mutant was only slightly decreased. 72 hpf, in situ hybridization, mpx probe. (M,N) The expression of rag1 in the thymus was reduced in the mutant. Day 4, in situ hybridization. (O–R) The expression of the vascular marker kdrl and arterial marker efnb2a was not significantly changed in the mutant, 30 hpf (S,T) Proliferation is decreased in the brain and blood of in the mutant embryo but cells in some other tissues continue to proliferate. 24 hpf. Antibodies to phosphorylated histone H3.