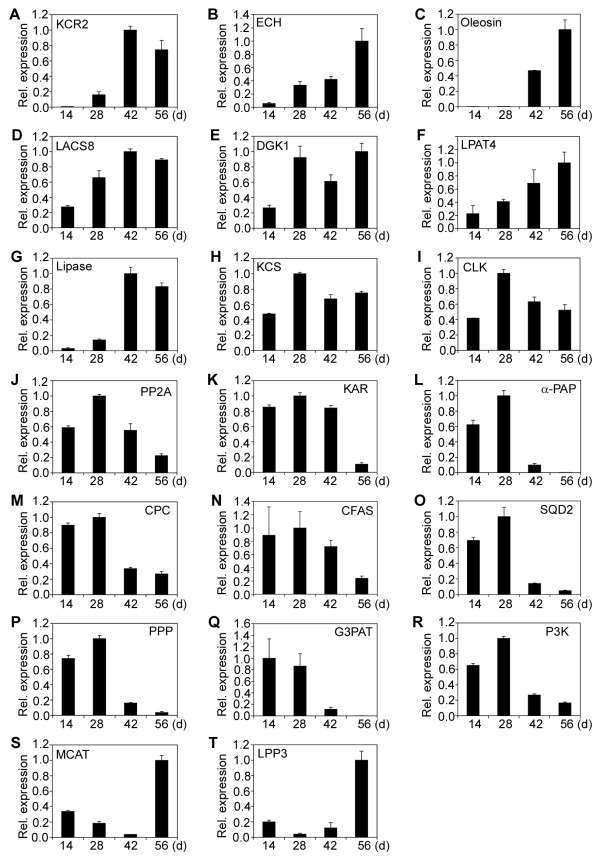
Figure 5.
Relative expression of fatty acid and lipid biosynthetic genes (III). (A) 3-ketoacyl-CoA reductase 2 (KCR2). (B) enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH). (C) Oleosin. (D) Long-chain acyl-CoA synthase 8 (LACS8). (E) Diacylglycerol kinase 1 (DGK1). (F) Lysophosphatidyl acyltransferase 4 (LPAT4). (G) Lipase. (H) Ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS). (I) Choline kinase (CLK). (J) Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). (K) Ketoacyl ACP reductase (KAR). (L) Phosphatidic aid phosphatase α (α-PAP). (M) Cholinephosphate cytidylyltransferase (CPC). (N) Cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase (CFAS). (O) Sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol synthase type-2 (SQD2). (P) Phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase (PPP). (Q) Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (G3PAT). (R) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (P3K). (S) Malonyl CoA ACP transacylase (MCAT). (T) Lipid phosphate phosphatase 3 (LPP3). The gene transcripts were measured by qRT-PCR. Results are shown as the relative expression of genes at different developmental stages by comparing to itself at the highest expression, which was set as “1”. The experiments were performed in triplicate and the data are presented as means ± SD.