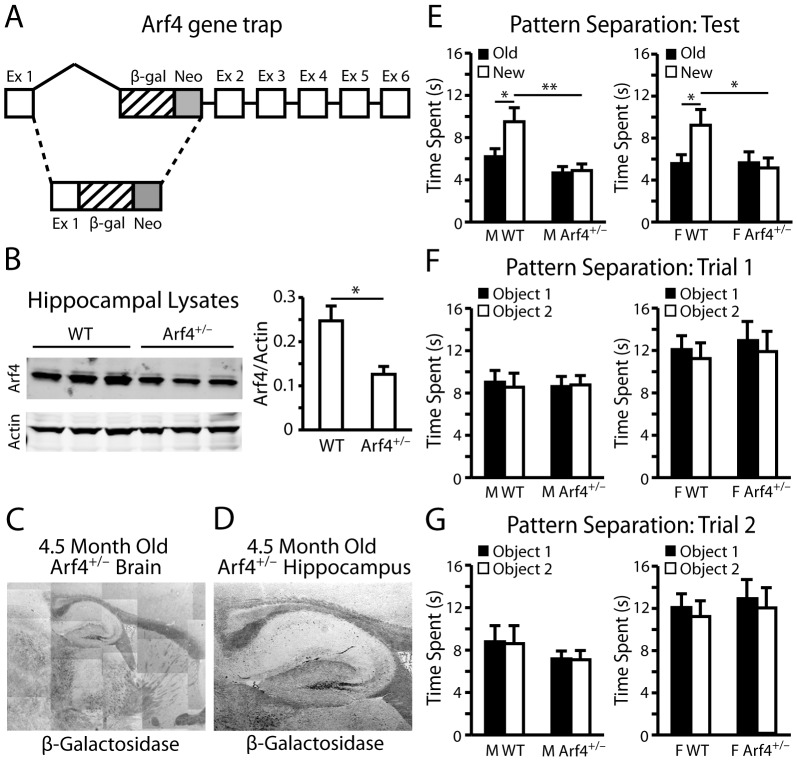
Figure 1. Arf4+/− mice are impaired in a dentate-gyrus dependent pattern separation task.
All mice were between 4–5 months of age at the time of experimentation. (A) A map of the Arf4 gene trapping construct obtained from BayGenomics (ES cell line CSH658). Ex, exon; β-gal, β-galactosidase gene; neo, neomycin-resistance gene. (B) Hippocampi from three WT and Arf4+/− littermate pairs were homogenized, followed by immunoblotting with anti-Arf4 (left panel). Actin loading controls are shown. Quantification of Arf4 protein levels in hippocampi prepared from WT or Arf4+/− mice (right panel). Arf4 protein levels were normalized to actin. (C) X-gal stained sagittal brain section from an Arf4+/− mouse at 5X magnification. (D) Representative image from a 4.5-month-old Arf4+/− hippocampus. (E) Quantification of the amount of time male (left panel) or female (right panel) WT and Arf4+/− mice spent exploring a novel object/context during a pattern separation task. (N = 12–13 mice per genotype per sex). (F–G) Quantification of the amount of time male (left panel) or female (right panel) WT and Arf4+/− mice spent exploring an object in a specific context during the first (F) or second (G) trial of the pattern separation task. All data are mean±SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01.