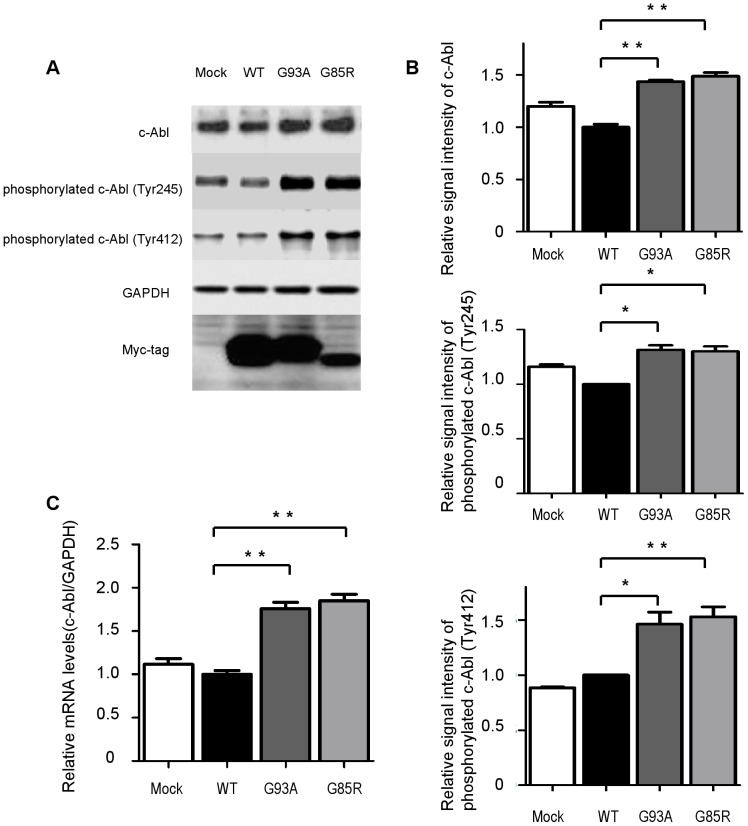
Figure 2. Activation of c-Abl caused by mutant SOD1 overexpression.
A: Total c-Abl and phospho-c-Abl (Tyr245 and Tyr412) protein levels in NSC-34 cells overexpressing human wild-type and mutant SOD1 protein were measured by western blotting. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. Cells were cultured with doxycycline (Dox, 2 µg/ml) in serum-free culture medium for 48 h. B: Densitometric analysis (n = 3 per group) of the results shown in Fig. 2A demonstrated that both types of mutant SOD1, G93A and G85R, significantly increased the amount of total c-Abl protein and facilitated phosphorylation at both c-Abl sites, Tyr245 and Tyr412. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post-hoc test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. C: Expression levels of c-Abl mRNA were measured by quantitative RT-PCR in NSC-34 cells overexpressing wild-type or mutant human SOD1 (n = 4 per group). Cells were cultured with doxycycline (Dox, 2 µg/ml) in serum-free culture medium for 48 h. Overexpression of both types of mutant SOD1 significantly increased the c-Abl mRNA level compared with overexpression of wild-type SOD1 (P<0.01). Data shown are ratios (mean ± SEM) of the c-Abl mRNA levels in NSC-34 cells overexpressing wild type SOD1 (n = 6). Statistics were evaluated using 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post-hoc test. **P<0.01.