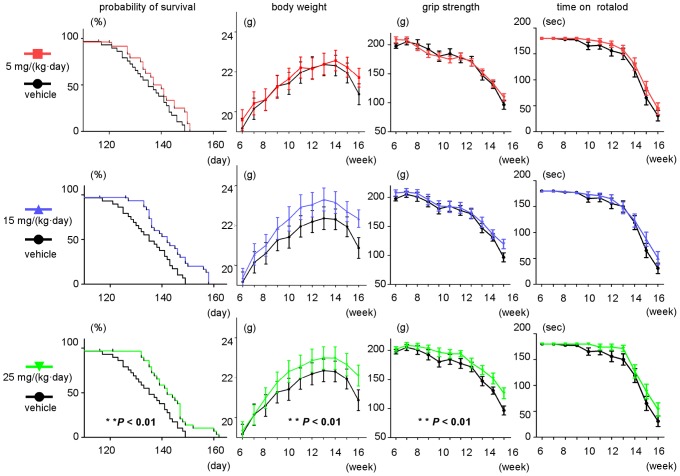
Figure 5. The effect of dasatinib on survival and disease progression in G93A mice.
Rotarod activity, grip strength, body weight, and survival rate in G93A mice with or without dasatinib treatment (0, 5, 15, and 25 mg/(kg·day)). Survival of G93A mice was improved by dasatinib at a dose of 25 mg/(kg·day) compared with vehicle treatment (Log-rank test, P<0.01, 25 mg/(kg·day) vs. vehicle), whereas a lower dose of dasatinib (5 mg/(kg·day)) had no significant effect on life span. Weight loss was also ameliorated by dasatinib at a dose of 25 mg/(kg·day) compared with vehicle treatment (2-way ANOVA, P<0.01, 25 mg/(kg·day) vs. vehicle). The administration of dasatinib at 25 mg/(kg·day) similarly ameliorated grip strength (2-way ANOVA, P<0.01, 25 mg/(kg·day) vs. vehicle). The difference in physical function between the groups as assessed by rotarod was not significant by 2-way ANOVA, although a beneficial tendency of dasatinib was observed.