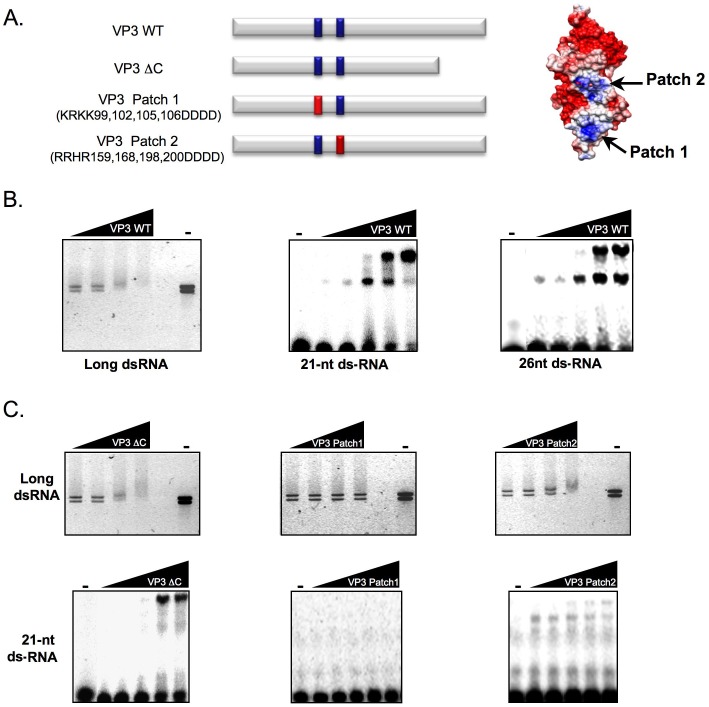
Figure 2. IBDV VP3 binds long and short dsRNAs, and the positively charged domain Patch 1 is involved in this interaction.
(A) Schematic representation of wild type IBDV VP3 and derivative mutants used in this assay (red bars indicate mutated patches). The distribution of electrostatic potential on VP3 surface (adapted from [56]) is shown at the right. Both Patch 1 and Patch 2 positively charged regions are indicated in blue, whereas negatively charged regions of the protein are shown in red. (B) (Left panel) Purified IBDV VP3 WT protein (final concentration of 10, 20, 40 and 80 nM) was incubated with the IBDV genomic dsRNAs. (Central and right panels) Purified IBDV VP3 protein (final concentration of 80, 160, 320, 640 and 1200 nM) was incubated with 32P-labelled 21-nt or 26-nt ds small RNAs. (C) (Upper panels) Purified VP3 ΔC (final concentration of 12, 24, 48 and 96 nM) and Patch 1 or Patch 2 mutant VP3 (final concentration of 10, 20, 40 and 80 nM) were incubated with IBDV genomic dsRNAs. (Lower panels) Purified VP3 ΔC (final concentration of 90, 180, 360, 720 and 1440 nM), and Patch 1 or Patch 2 mutant VP3 (final concentration of 80, 160, 320, 640 and 1200 nM) were incubated with 32P-labelled 21-nt small RNAs. In both B and C, protein-IBDV genomic dsRNA complexes were resolved in agarose gels, stained with EtBr, and photographed under UV light, and protein-small RNA complexes were resolved in polyacrylamide gels and revealed by autoradiography.