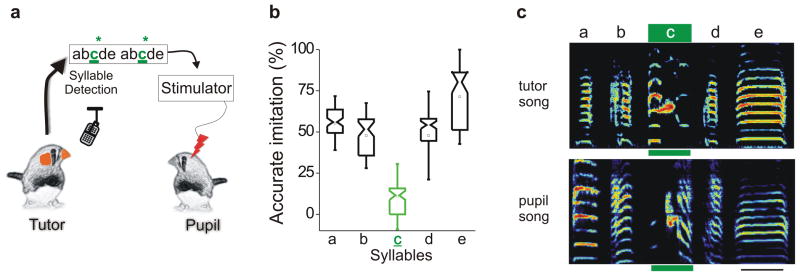
Figure 3. Tutor song syllable-triggered microstimulation of HVC disrupts copying of the targeted syllable.
a, Sketch of the experimental design in which the pupil’s HVC is microstimulated (20μA per HVC, biphasic pulses, 300 μs each phase at 170Hz for 200ms) while the tutor is singing syllable ‘c’. b, Pupils fail to imitate the syllable paired with HVC microstimulation (syllable c; F(4,14) = 7.508, P = 0.001; n = 4 birds; notched box plot whiskers = 1.5 standard deviations). c, Sonograms of the tutor’s song and the adult song of one his pupils that was microstimulated in HVC when the tutor sang syllable ‘c’. Green bar under syllable ‘c’ and scale bar at lower right = 130ms; ordinate = 0 – 9 kHz.