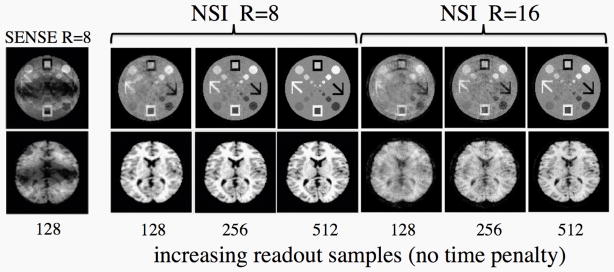
Fig. 6.
Simulations demonstrating the effect of increasing the readout sampling in NSI. Imaging time is held constant. The NSI method benefits from the increase in sampling in the readout due to the 2D nature of the encoding fields whereas in the case of Cartesian sampling there is no reduction in the foldover artifacts with increasing sampling in the readout. With an algebraic construction scheme, additional data contributes information towards the image. In practice, increasing the readout samples is limited by gradient strength and bandwidth or noise issues but the range simulated here is well within reach of clinically relevant gradient amplitudes. This example shows that increased sampling in the readout allows for very high acceleration factors to be obtained while still maintaining excellent image quality.