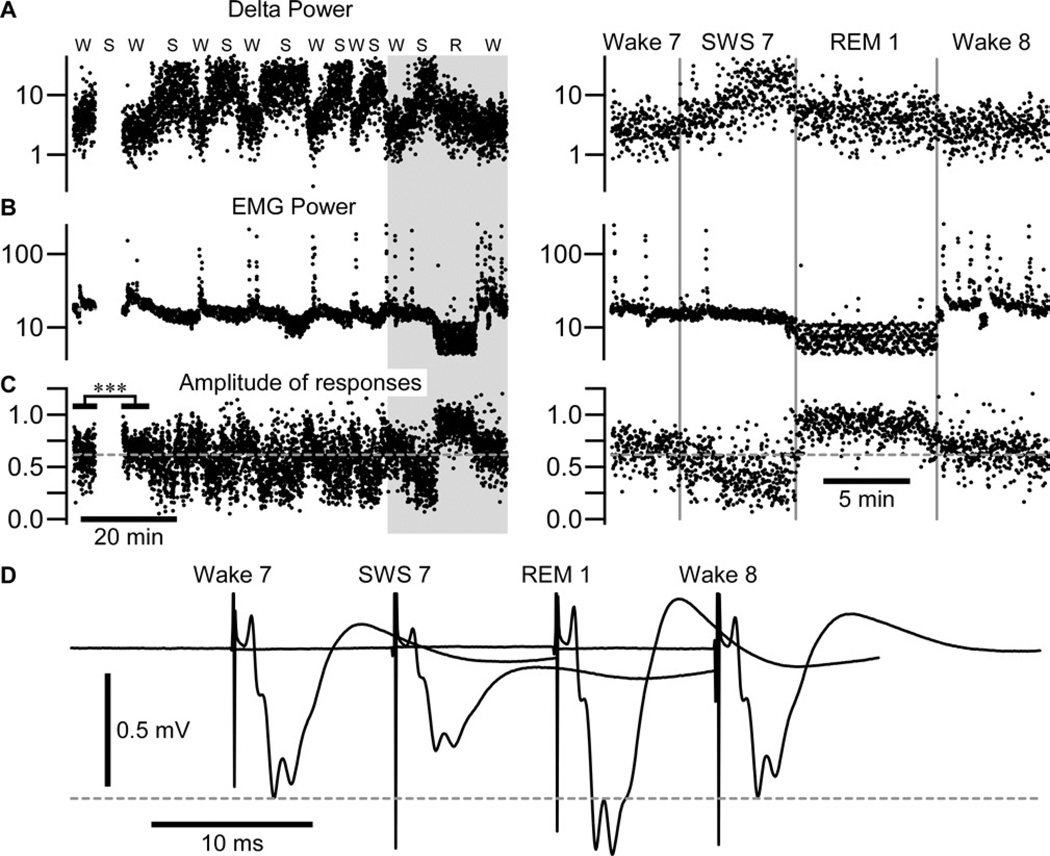
Figure 2. REM sleep does not potentiate somatosensory evoked potential in a following wake episode.
The delta power calculated from an area 7 local field potential (A) and EMG power (B) calculated around each medial lemniscal stimulus (±500 ms).
(C) The amplitude of somatosensory evoked potential. W – Wake, S – SWS, R – REM sleep. Note that no stimulation was delivered during the first slow-wave sleep episode and that responses were very significantly enhanced in the second wake episode as compared to the first wake episode; ***p<0.001, unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. The right panel corresponds to the shaded area in (A, B, C) expanded. The amplitude of response was not enhanced after late REM sleep; p=0.7, unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction.
(D) Averaged response in each state of vigilance from wake 7 to wake 8 as indicated.