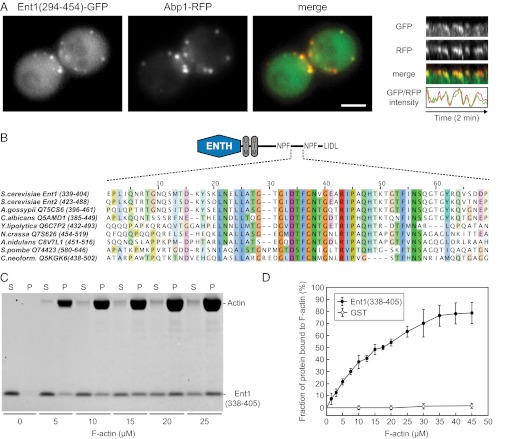
Fig. 4.
Identification of the Ent1 F-actin binding domain. (A) Colocalization of Ent1(294–454)-GFP with Abp1-RFP at endocytic sites. (Left) Separate channels and the merged image of an ABP1-RFP strain expressing Ent1(294–454)-GFP from a plasmid. (Right) Kymographs and fluorescence intensity profiles of Ent1(294–454)-GFP and Abp1-RFP at a single endocytic patch. Kymographs are oriented with the cell exterior at the top. (Scale bar: 2 μm.) (B) The multiple sequence alignment of the ACB region of S. cerevisiae Ent1, Ent2, and epsin proteins from indicated species. For each sequence the UniProt accession number and the amino acids aligned are indicated. (C) Ent1(338–405) binds to F-actin in the actin cosedimentation assay. Recombinant Ent1(338–405) protein (5 μM final concentration) was incubated with increasing amounts of F-actin. The fractions of unbound (S) and F-actin–bound protein (P) are shown. (D) Quantification of Ent1(338–405) binding to F-actin. The binding of Ent1(338–405) protein or GST control to F-actin was analyzed as in C. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments).