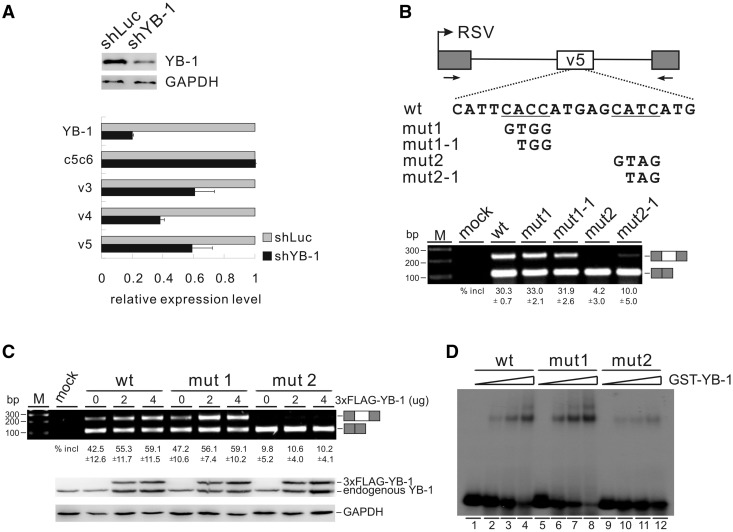
Figure 4.
YB-1 binds to a CAUC motif in CD44 variable exon v5 and stimulates exon v5 splicing. (A) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of CD44 variable exons v3, v4 and v5, as well as of constitutive exons c5 and c6 (c5c6) in MDA-MB-231 cells stably transfected with control (luciferase) or YB-1 shRNA. β-Actin served as a reference gene for qRT-PCR. The mRNA expression levels of YB-1 and CD44 exons in YB-1 knock-down cells were normalized to those in control knock-down cells. The YB-1 knock-down efficiency was determined by western blotting with GAPDH as a control. (B) Upper panel: schematic representation of CD44 exon v5 minigene constructs. The CD44 genomic sequence from 794 nt upstream of exon v4 to 479 nt downstream of exon v5 (exon v4 sequence was deleted in this minigene, see Materials and Methods) was inserted into pET01. Exon v5 is represented by a white box, and flanking insulin exons by gray boxes. The potential YB-1-binding sites are underlined. Lower panel: RT-PCR analysis of in vivo splicing pattern of wild-type, mut1, mut1-1, mut2 and mut2-1 constructs transfected into HEK 293 cells. As a control, no DNA was transfected (mock lane). The averages of exon inclusion percentage with standard deviations are shown below (n = 3). (C) RT-PCR analysis of splicing activity of the wild-type, mut1, and mut2 minigene constructs, which were co-transfected with increasing amounts of FLAG-tagged YB-1 expression constructs (0, 2 and 4 µg) in HEK 293 cells. The averages of exon inclusion percentage with standard deviations are shown below (n = 3). The expression level of YB-1 was detected by western blotting, and GAPDH served as a loading control. (D) Gel shift analysis of YB-1 binding affinities to RNAs derived from wt, mut1 and mut2 constructs. Complexes were formed by incubation of 32P-labeled short RNAs with 0-, 25-, 50- and 100-fold molar excess of GST-YB-1 fusion proteins.