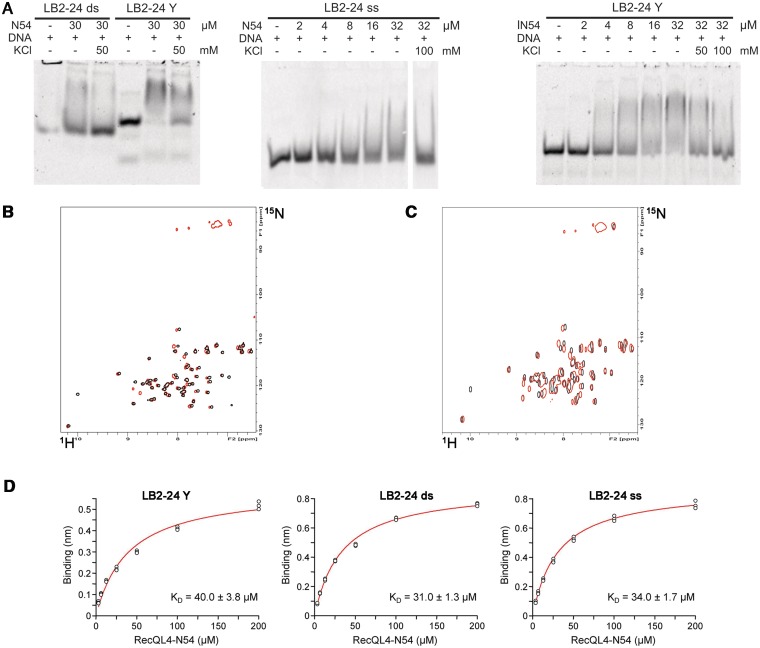
Figure 7.
RecQL4_N54 binding to Y-shaped DNA. (A) RecQL4_N54 prefers binding to Y-shaped DNA over ssDNA and dsDNA. Left panel: 30 µM RecQL4_N54 was preincubated in the presence of 2 µM of the indicated DNA and the DNA–protein complexes resolved by electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay. Middle panel: ssDNA binding—indicated amounts of RecQL4_N54 were preincubated with 1.3 µM oligomer LB2-F carrying a 5′-fluorescein, and the DNA–protein complexes resolved by electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay. Right panel: Binding to Y-shaped DNA—indicated amounts of RecQL4_N54 were preincubated with 2 µM LB2-derived Y-shaped DNA, and the DNA–protein complexes resolved by electrophoretic mobility gel shift assay. The DNA binding buffer was supplemented with KCl as indicated. Details for the DNA fragments are provided in Supplementary Table S1. (B) [1H,15N]–HSQC spectra (15N chemical shifts in F1 and 1H chemical shifts in F2) of RecQL4_N54 (200 µM) without (black contours) and with 3.5-fold excess (red contours) of Y-shaped DNA. (C) [1H,15N]-HSQC spectra of RecQL4_N54 (200 µM) without (black contours) and with 2-fold excess (red contours) of ssDNA. (D) Real-time binding analysis of RecQL4_N54 to Y-shaped, dsDNA and ssDNA. Fits of the biolayer interferometry steady-state binding of RecQL4_N54 using a HEPES buffer containing 50 mM NaCl.