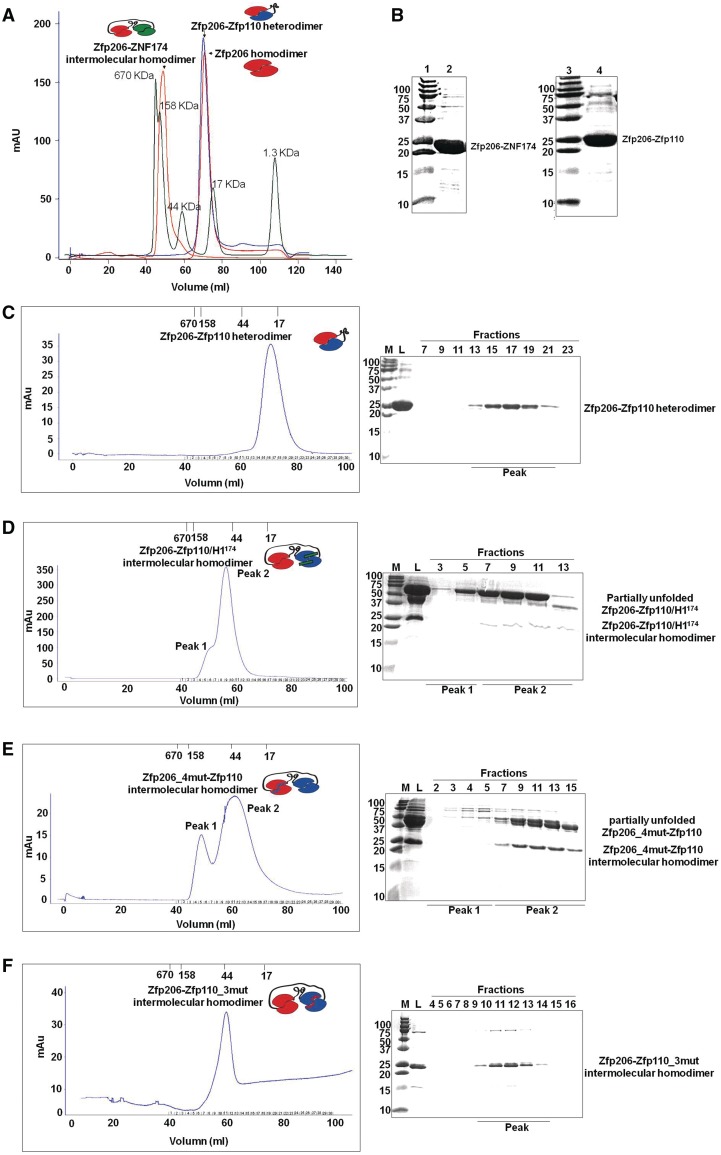
Figure 4.
Role of the amino-terminal helix 1 for Zfp206SCAN and Zfp110SCAN heterodimerization and mutations based on the Zfp206SCAN-Zfp110SCAN heterodimer. (A) The intramolecular linker-mediated Zfp206-Zfp110 heterodimer elutes at the volume corresponding to the theoretical molecular weight of a monomeric fusion protein 23 KDa, which is virtually identical with the elution profile of un-connected Zfp206SCAN homodimer (21 KDa). Oppositely, the Zfp206-ZNF174 elutes at the volume corresponding to a higher molecular weight indicating the formation of an intermolecular homodimer. The profile of a molecular weight standard is overlaid as green curve. (B) 15% SDS–PAGE gel shows purified Zfp206-ZNF174 (lane 2) and Zfp206-Zfp110 (lane 4) and molecular standards (lane 1 and 3; weights in kilo Daltons). (C) Elution profile of the linker mediated intramolecular Zfp206-Zfp110 heterodimer (left) and SDS–PAGE of the eluted fractions (right). (D) Elution profile of the Zfp206-/Zfp110_H1174 protein suggesting the formation of an intermolecular homodimer instead of the linker-mediated heterodimer seen in (C). Cartoon drawing of the various complexes are shown as inset of the chromatograms with the Zfp206SCAN in red, the Zfp110SCAN in blue and the ZNF174SCAN in green. The linker is illustrated with a black line and the helix1 of the ZNF174SCAN that was introduced into the Zfp110SCAN is shown as green bar. (E) Zfp206-4mut-Zfp110 intermolecular homodimer (Zfp206SCANI48AL49AR13AR31A-Zfp110SCAN) and (F) Zfp206-Zfp110-3mut intermolecular homodimer (Zfp206SCAN-Zfp110SCANC36AL40AL51A).