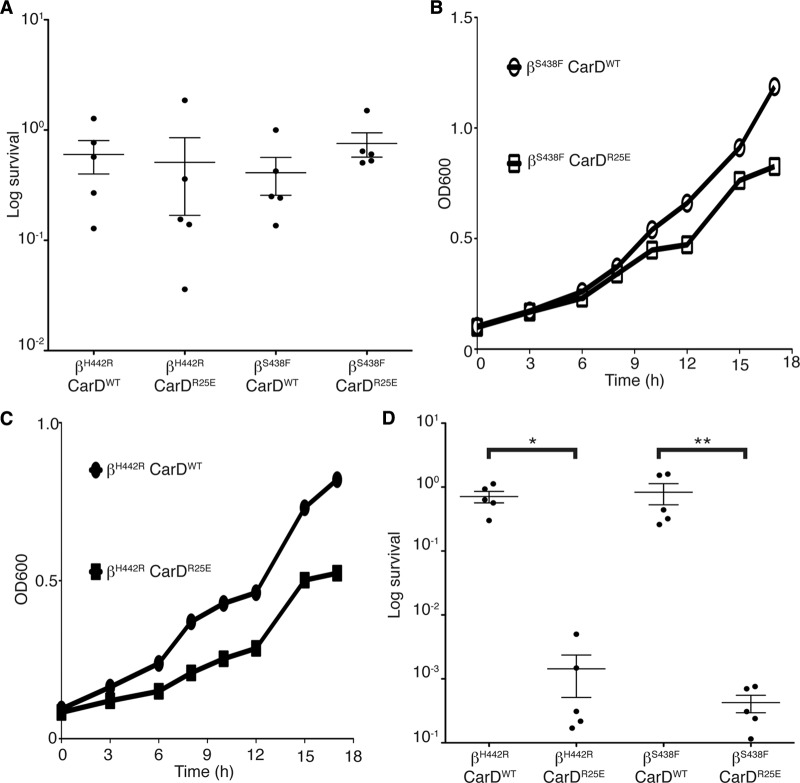
Fig 7.
Rifampin-resistant mutants are still sensitive to interference with the CarD/RNAP interaction. (A) Survival of M. smegmatis strains during rifampin treatment. The M. smegmatis strains resistant to rifampin due to substitutions in RNAP β at either position S438 (βS438F) or H442 (βH442R) were engineered to express either CarDWT or CarDR25E. The log-phase βS438F CarDWT, βS438F CarDR25E, βH442R CarDWT, and βH442R CarDR25E cultures in LB were treated for 1 h with 500 μg/ml in rifampin. After treatment, dilutions were plated on LB, and survival was determined as a ratio of CFU after treatment to that in untreated cultures. The graph shows the mean ± SEM, and each sample is represented by a black circle. (B and C) Representative growth curves from 4 replicates each of M. smegmatis βS438F CarDWT (open circles), βS438F CarDR25E (open squares), βH442R CarDWT (closed circles), and βH442R CarDR25E (closed squares) in LB. (D) Survival of M. smegmatis strains during H2O2 treatment. The log-phase M. smegmatis βS438F CarDWT, βS438F CarDR25E, βH442R CarDWT, and βH442R CarDR25E cultures were treated for 1 h with 25 mM H2O2. After treatment, dilutions were plated on LB, and survival was determined as a ratio of CFU after treatment to that in untreated cultures. The graph shows the mean ± SEM, and each sample is represented by a black circle. The significance levels were determined as described for Fig. 3.