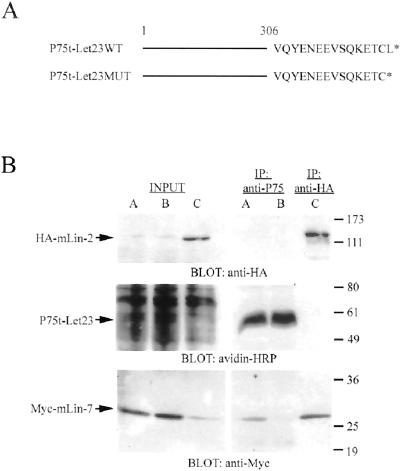
Figure 1.
Differential binding of mLin-7 to the chimeric receptors. (A) Schematic representation of the NGFR/P75 chimeric receptor constructs. Amino acids 1–306 of the NGFR/P75 (truncated after the transmembrane domain) were fused to the carboxyl-terminal amino acids of LET-23 (shown in single letter code) to form the P75t-Let23WT construct. The P75t-Let23MUT construct deletes the final amino acid in the LET-23 carboxyl terminus, destroying the mLin-7 PDZ domain ligand. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids as follows: lanes A, pRK5Myc-mLin-7 plus pP75t-Let23WT; lanes B, pRK5Myc-mLin-7 plus pP75t-Let23MUT; lanes C, pRK5Myc-mLin-7 plus pcDNA-3HA-mLin-2. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were surface biotinylated, and then lysates were collected for immunoprecipitation with anti-P75 or anti-HA antibodies, as indicated. Precipitated proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and the membrane was probed with avidin-HRP (to detect surface biotinylated P75t-Let23), anti-HA, or anti-Myc antibodies. The input lanes contain approximately one-tenth the amount of HEK293 lysate used in the precipitation experiments. The arrows indicate the relevant bands on the immunoblots. Relative molecular weight is shown to the right in kilodaltons.