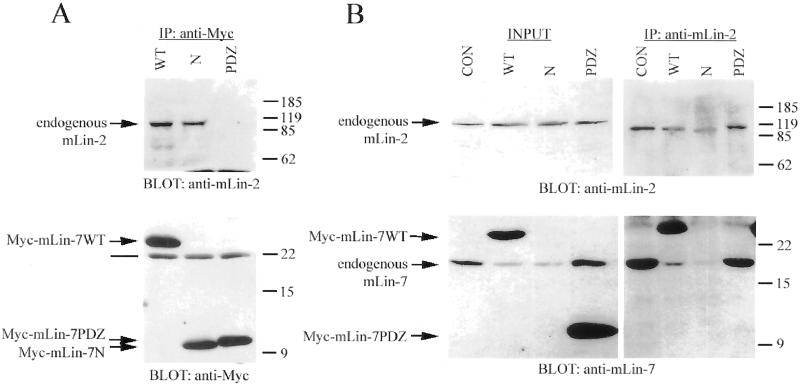
Figure 4.
Myc-mLin7N competed with endogenous mLin-7 for binding to endogenous mLin-2 in MDCK cells. (A and B) Precipitation analysis of MDCK cell lines expressing Myc-tagged mLin-7 constructs (described in the legend to Figure 3). Triton lysates were collected for immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies. Precipitated proteins were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and the membrane was probed with antibodies as indicated. (A) Immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibodies and coprecipitation of endogenous mLin-2. Top panel was immunoblotted with anti-mLin-2 antiserum. Bottom panel was immunoblotted with anti-Myc antibodies. (B) Immunoprecipitation with anti-mLin-2 antiserum and coprecipitation of endogenous mLin-7. Top panels were immunoblotted with anti-mLin-2 antiserum. The exposure of the left top panel was three times that of the right top panel. Bottom panels were immunoblotted with purified anti-mLin-7 antibodies. Note that the anti-mLin-7 antibodies are primarily immunoreactive to the mLin-7 PDZ domain and do not significantly recognize the amino terminus of mLin-7. Lanes in A and B are CON, mock-transfected MDCK cells; WT, stably expresses Myc-mLin-7WT; N, stably expresses Myc-mLin-7N; and PDZ, stably expresses Myc-mLin-7PDZ. The INPUT lanes contain approximately one-tenth the amount of lysate used in the precipitations. Arrows indicate the relevant bands on the immunoblots. The line in A indicates the light chain of the antibody used in the precipitation. Relative molecular weight is shown to the right in kilodaltons.