Table 2.
Use of a 20-member validation library to probe the reaction scope.
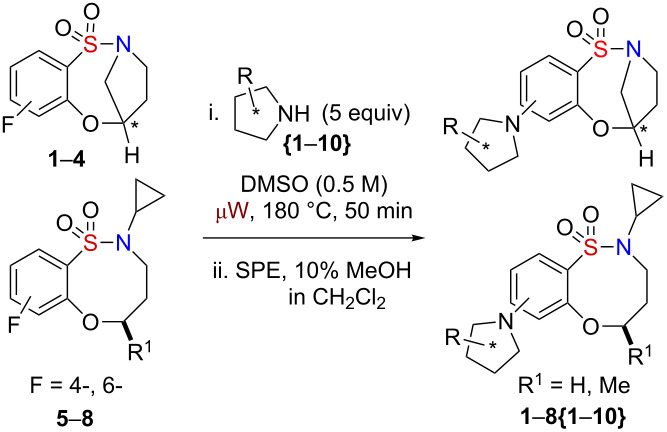 | |||||||
| Sultama | Purity (%)b | Yield (%)b | Quantity (mg) | Sultama | Purity (%)b | Yield (%)b | Quantity (mg) |
| 1{3} | 99.8 | 78 | 79.5 | 5{1} | 100 | 80 | 79.8 |
| 2{3} | 99.4 | 69 | 70.0 | 5{2} | 100 | 80 | 79.4 |
| 3{3} | 100 | 48 | 49.3 | 5{3} | 100 | 76 | 75.8 |
| 4{3} | 99.7 | 53 | 54.1 | 5{4} | 100 | 79 | 79.1 |
| 1{1} | 100 | 71 | 71.7 | 5{5} | 100 | 83 | 85.7 |
| 1{2} | 100 | 72 | 73.4 | 5{6} | 100 | 80 | 83.1 |
| 1{4} | 99.8 | 75 | 76.7 | 5{7} | 98.2 | 17 | 18.7c |
| 1{5} | 99.7 | 69 | 73.6 | 5{8} | 99.9 | 46 | 49.2 |
| 1{6} | 99.6 | 85 | 90.2 | 5{9} | 99.1 | 79 | 85.3 |
| 1{8} | 100 | 86 | 94.9 | 5{10} | 99.1 | 78 | 83.7 |
aReaction conditions: benzoxathiazocine 1,1-dioxides 1–8 (1 equiv, 80 mg), dry DMSO (0.5 M) and amine (5 equiv.); bpurified by automated preparative reverse phase HPLC (detected by mass spectroscopy); purity was assessed by HPLC (214 nm); cthe low yield obtained was due to instrumental error (see Supporting Information File 1 for more information).
