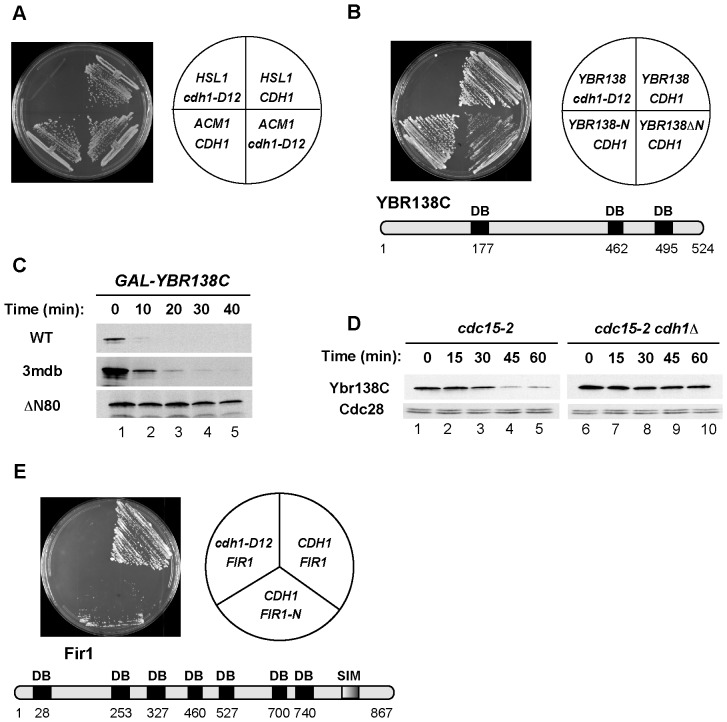
Figure 3. Degradation of Ybr138C and Fir1 and their interaction with Cdh1.
(A)Two hybrid assay to detect Cdh1-substrate interactions. The bait in this assay was either wild-type Cdh1-ΔN200 or Cdh1-ΔN200-D12, which contains mutations within Cdh1's WD40 domain previously demonstrated to disrupt Cdh1's interaction with the substrate D-Box [37], [41]. The prey consisted of the APC/C substrate Hsl1 or the APC/C pseudosubstrate inhibitor Acm1 [37]. (B) Yeast two-hybrid interaction between Cdh1 and Ybr138C. Cells expressing Cdh1 or Cdh1-D12 and Ybr138C, Ybr138C-ΔN200, or Ybr138C-N270 were tested for growth on selective medium, which indicates interaction of the respective proteins. Bottom: Schematic representation of Ybr138C indicating positions of potential D-boxes (DB). (C) Degradation of Ybr138C requires its N-terminal region but not putative D-boxes. Cells expressing wild-type YBR138C, YBR138C-3mdb, and YBR138C-ΔN80 from a GAL1 promoter were arrested in G1 and induced with galactose. Samples were withdrawn at the indicated times after cycloheximide addition and processed for blotting with PAP antibodies as in Fig. 2A. (D) cdc15-2 and cdc15-2 cdh1Δ cells carrying endogenous YBR138C-TAP were synchronized in mitosis by incubation at 37°C for 3 hours and released at 23°C at time zero. Samples were withdrawn at the indicated times and processed for immunoblotting. Cdc28 was used as a loading control. (E) Yeast two-hybrid interaction between Cdh1 and Fir1. As in (B) but cells carried Fir1 or Fir1-N200 instead of Ybr138C. Bottom: Schematic of Fir1 indicating its potential D-boxes (DB) and its SUMO-interacting motif (SIM).