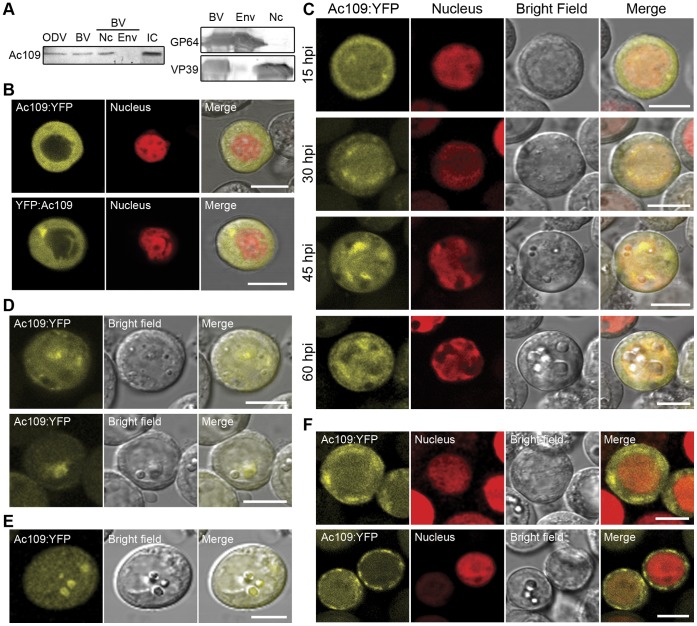
Figure 2. Ac109 localization in virions and in Sf-9 cells.
(A) Western blot analysis of purified virions. Budded viruses (BVs), obtained from supernatants of Sf-9 cells infected with wild type (wt) AcMNPV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.1, were purified through a 25% w/v sucrose followed by a 25–65% sucrose gradient. Purified BVs were resuspended in PBS, and nucleocapsids and envelopes were separated using 1% IGEPAL and ultracentrifugation through a glycerol cushion. Occlusion derived viruses (ODVs) were obtained after alkaline treatment of polyhedra recovered from the infected Sf-9 cells. ODVs were purified through a discontinuous 30–65% sucrose gradient. Ac109, GP64 and VP39 proteins were detected from purified ODVs, BVs, BVs envelopes (Env) and nucleocapsid (Nc) fractions with a polyclonal serum anti Ac109-GST fusion protein, an anti-GP64 monoclonal antibody or an anti-VP39 monoclonal antibody. Sf-9 cells infected with wt AcMNPV (IC) were used as a control of Ac109 detection. (B) Subcellular localization of Ac109 in living cells. Ac109 fused to YFP protein at either C or N-terminus (Ac109:YFP and YFP:Ac109) and transcribed from pOpIE2 promoter was detected in Sf-9.RNuc cells by confocal microscopy at 48 h post-transfection (hpt). (C) Kinetics of subcellular localization of Ac109 during baculovirus infection. Confocal microscopy of Sf-9.RNuc cells infected with Acppolp109-109Y virus at a MOI of 5 is shown at indicated h post-infection (hpi). Ac109 was fused to YFP at the C-terminal end (Ac109:YFP) and transcribed from the ac109 promoter. (D) Living insect cells infected with Acppolp109-109Y virus showing a heterogeneous Ac109:YFP accumulation around forming polyhedra in the nucleus. (E) Ac109:YFP fluorescence concentrated in the already formed polyhedra. (F) Cytoplasmic accumulations of Ac109:YFP in Sf-9.RNuc cells at different stages of viral infection. Bars represent 10 µm.