Figure 7. In vivo detection of CBCs with Ab-conjugated NPs and magnet-induced CBC capturing and signal amplification.
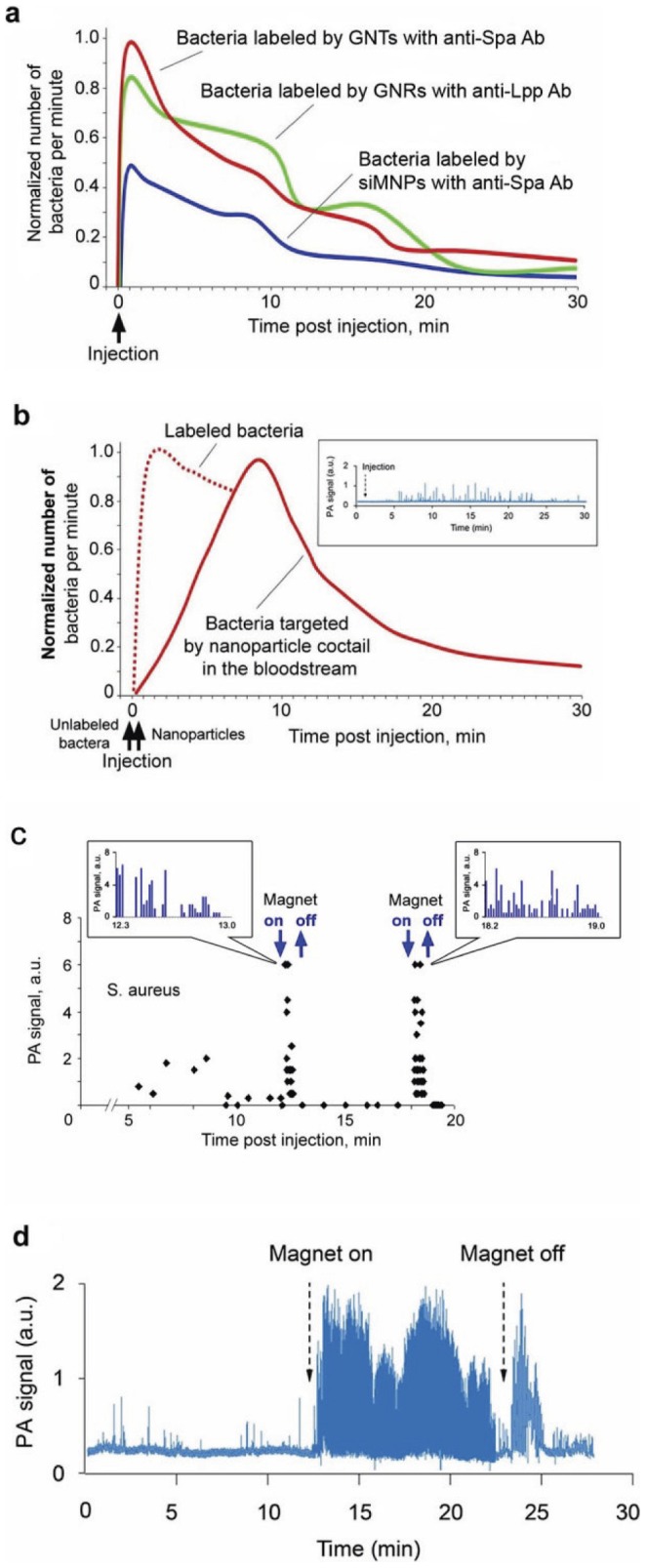
(a) In vivo PA monitoring of CBCs labeled with Ab-functionalized NPs in vitro prior to injection. (b) PA monitoring of CBCs labeled in vivo with a cocktail of functionalized NPs consisting of GNRs690 with anti-Lpp Ab and GNRs900 with anti-Spa Ab in a 50%∶50% proportion in 20 µL of phosphate-buffered saline (n = 3). The inset shows typical PA signal traces. Dashed line indicates PA monitoring observed when the same cocktail was used to label S. aureus cells in vitro prior to injection (similar to Fig. 7a). The average standard deviation for each time point in (a) and (b) is 18% (c) Verification of magnetic amplification of PA signals from bacteria labeled with 30-nm MNPs with anti-Spa Ab in rat mesentery. The inset shows typical PA signal traces. (d) In vivo real-time monitoring of PA signal dynamic from bacteria labeled in vivo by siMNPs with anti-Spa Ab before, during, and after magnetic field action in mouse ear. Laser parameters: wavelengths, 671 nm and 820 nm (a, b), 639 nm (c), 671 nm (d); energy fluence, 0.1 J/cm2.
