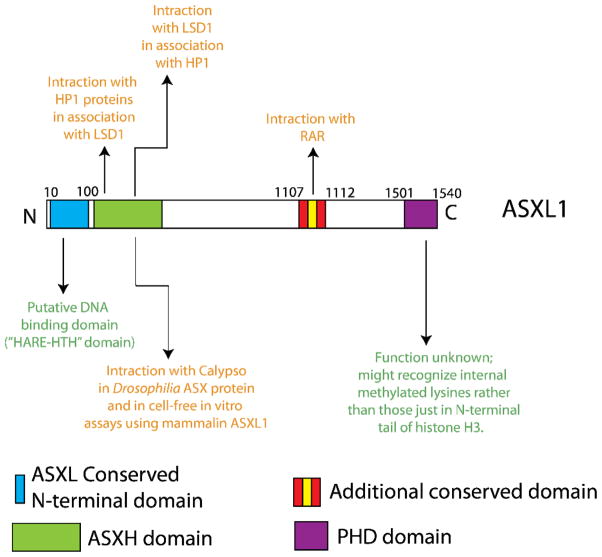
Figure 3. Conserved domains of mammalian Asxl proteins and possible functions of ASXL1.
ASXL1 contains a globular N-terminal domain which is conserved amongst ASX proteins and contains a potential DNA binding motif based on homology with other proteins of known function. This domain has been referred to as a HARE-HTH domain (HB1, ASXL1, restriction endonuclease helix-turn helix domain). Just distal to this domain is a domain which has been shown to bind Calypso (the mammalian homologue of BAP1) and serve as a deubiquitinase for histone H2A lysine 119. This activity has been shown in vivo in Drosophila and in cell-free assays using human ASXL1 purified protein. This same domain has also been suggested to bind to HP1 proteins and LSD1 (this activity has never been studied in a hematopoietic context). Distal to these domains lies a conserved domain which has been suggested to physically interact with the retinoic acid receptor (another activity which has never been verified in hematopoietic cells). Finally, a plant homeofinger domain (PHD domain) lies at the extreme C-terminus of all ASXL proteins. The function of this PHD domain has not yet been identified.