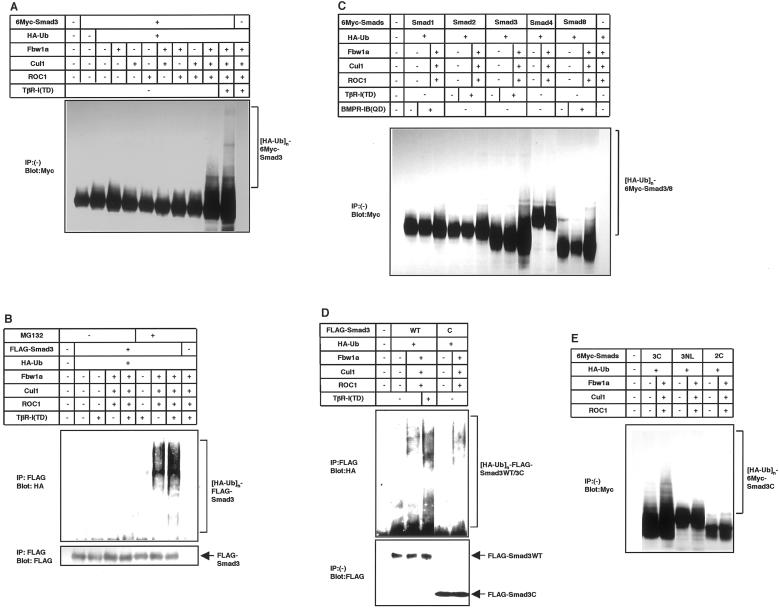
Figure 3.
Ubiquitination of Smad3 by the ROC1-SCFFbw1a complex in vivo. (A and B) Ligand-dependent ubiquitination of Smad3 is induced by the ROC1-SCFFbw1a complex. COS7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. For the detection of ubiquitinated proteins, cells were treated with 50 μM MG132 for 4 h before cell lysis unless indicated. Lysates from cells were directly subjected to anti-Myc immunoblotting (A) or subjected to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation followed by anti-HA immunoblotting (B). Expression levels of Smad3 are shown in the bottom (B). Polyubiquitination species of Smad3 are indicated ([HA-Ub]n-6Myc or FLAG-Smad3). (C) Smad3 and Smad8 are preferentially degraded by the ROC1-SCFFbw1a complex. COS7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, and ubiquitination was determined as in A. A short version of Smad8 lacking a part of linker region was used in the present study. (D and E) Ubiquitination occurs on the MH2 domain of Smad3. In D, COS7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with MG132, and ubiquitination was detected as in B. Expression levels of wild-type (WT) Smad3 and Smad3C are shown at the bottom. In E, ubiquitination of Smad3C was compared with that of Smad3NL and Smad2C containing the MH2 domain of Smad2 in transfected COS7 cells as in A.