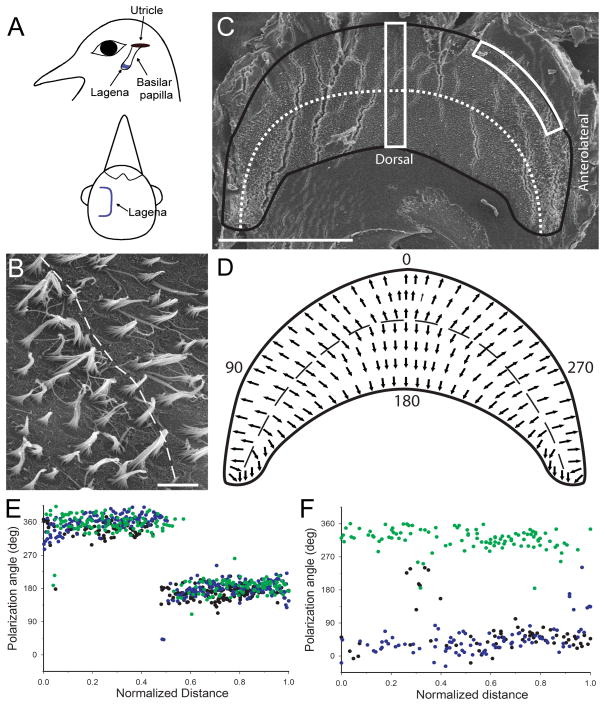
Figure 1.
Lagena orientation and receptor morphological polarization. A) Schematic illustration of lagena location and orientation in homing pigeons. The lagena lies vertical in the head at the apical end of the basilar papilla. The parasagittal central surface bends into two equal regions on either side that are directed laterally. B) Central lagenar hair cell stereocilia have opposite polarities directed away from the reversal line (dashed). C) Flattened left lagenar receptor surface (produced stress cracks in the epithelium) with border (black line) and reversal line (dotted) illustrated. Two counting frames (white boxes) were used for quantification of hair cell polarization. D) Schematic diagram of lagenar receptor epithelium showing morphological polarizations (arrows) and reversal line (dashed). Polarization directions were quantified, with the quadrant directions of 0° (ventral), 90° (postero-lateral), 180° (dorsal), and 270° (antero-lateral). E) Hair cell polarizations for all cells quantified in the central counting frame for 3 lagenas (green, black, blue dots) plotted as a function of normalized distance across the epithelium. F) Polarizations from the same 3 lagenas for all cells contained in the antero-lateral edge counting frame (green) or postero-lateral edge (black and blue). Scale bars: 500μm in A, C; 5μm in B.