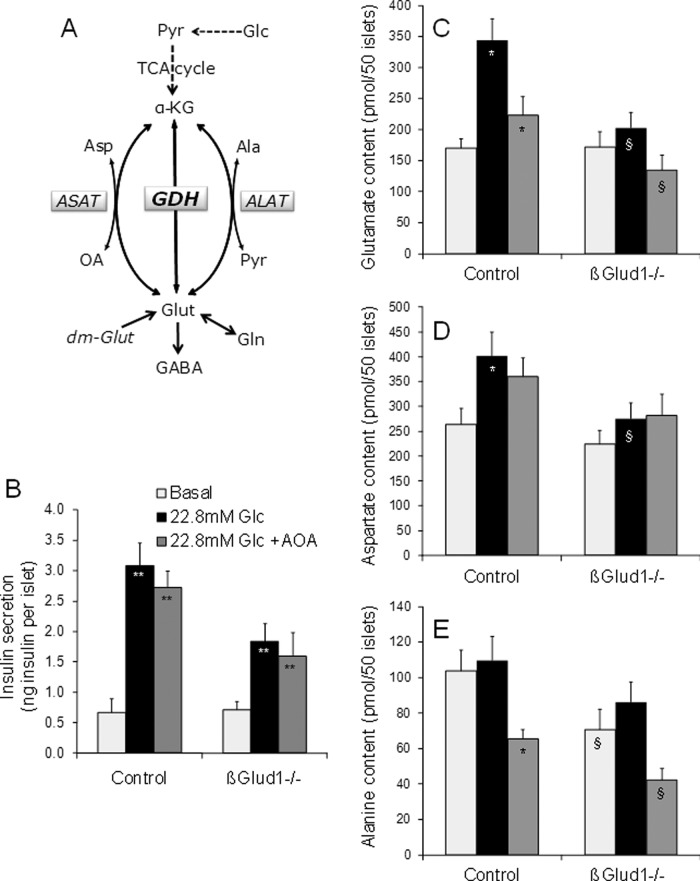
FIGURE 5:
Respective roles of GDH and aminotransferases in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. (A) GDH and aminotransferases (ASAT and ALAT) connect glutamate (Glut) and the TCA cycle intermediate α-KG. ASAT uses either oxaloacetate (OA) or aspartate (Asp) as a cosubstrate and ALAT uses either pyruvate (Pyr) or alanine (Ala), along with Glut or α-KG, respectively. Glutamate can also arise from glutamine (Gln) deamidation. (B–E) After an overnight culture in RPMI-1640 medium, islets isolated from control and βGlud1−/− mice were handpicked and preincubated for 1 h in glucose- and glutamine-free RPMI-1640 medium. Then islets were incubated for 1 h at 2.8 mM (Basal) and 22.8 mM (Glc) glucose in the absence or presence of 2 mM AOA. At the end of the assay period, supernatants were collected to measure insulin secretion (B) and islets were collected in 5% (wt/vol) 5-sulfosalicylic acid before determination of amino acid concentrations by HPLC (C–E). Values are means ± SE of six independent mice for each group. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01 vs. basal of corresponding genotype; §, p < 0.05, §§, p < 0.01 vs. control under corresponding stimulation condition; #, p < 0.01 vs. 22.8 mM Glc of corresponding genotype.