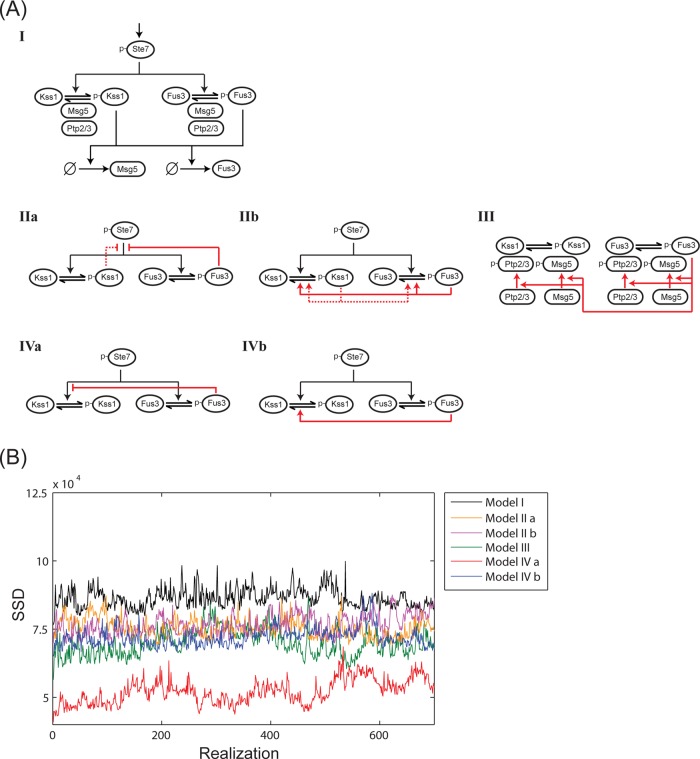
FIGURE 2:
Six models of Fus3-mediated attenuation of Kss1 activity. (A) I, A schematic diagram of the pathway elements common to all six models. All the models include the positive regulator Ste7 and MAP kinase–dependent induction of Msg5 and Fus3. The phosphatases Ptp2 and Ptp3 are also present in all six models. II–IV, models representing different mechanisms of regulation (red lines and arrows). Model IIa states that Fus3- (and Kss1-) dependent negative feedback decreases activation of both Fus3 and Kss1. Model IIb states that Fus3- (and Kss1-) dependent negative feedback increases deactivation of both Fus3 and Kss1. Model III states that Fus3 phosphorylates and activates all three phosphatases, Ptp2, Ptp3, and Msg5. Model IVa states that the rate of Kss1 phosphorylation and activation (Kss1 conversion to p-Kss1) is inversely proportional to the amount of active Fus3 (p-Fus3). In this model, the phosphatases Msg5 and Ptp2/3 are constitutively active. Model IVb states that Kss1 inactivation is proportional to active Fus3. Again the three phosphatases are taken to be constitutively active. (B) The SSD between the experimental data and output of the six models vs. the number of accepted realizations in the Monte Carlo optimization routine. A smaller SSD indicates a better fit to the data.