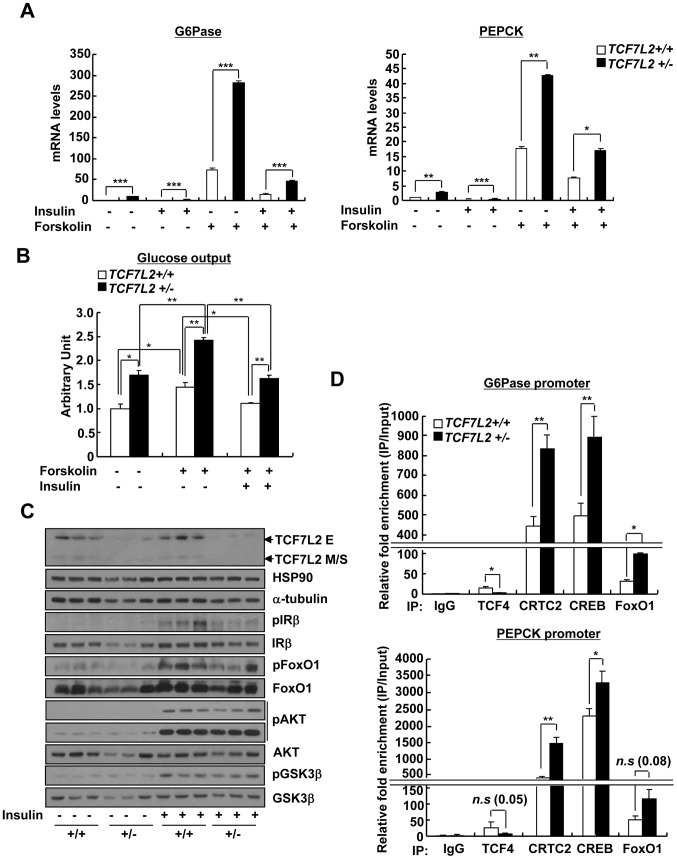
Figure 6. Chronic depletion of TCF7L2 promotes increased glucose production and gluconeogenic gene expression in hepatocytes.
A) Q-PCR analysis showing effects of forskolin (10 µm, 2 h) and insulin (100 nM, 12 h) on expression levels of gluconeogenic genes in primary hepatocytes from TCF7L2 +/+ and TCF7L2 +/− mice (n = 3 for each group). Representative data from at least three independent experiments are shown. B) Glucose output assay showing the effects of TCF7L2 levels on glucose production between primary hepatocytes from TCF7L2 +/+ or TCF7L2 +/− mice was performed as described in Materials and Methods (n = 3 for each group). Representative data from at least three independent experiments are shown. C) Western blot analysis showing insulin signaling in primary hepatocytes from TCF7L2 +/+ and TCF7L2 +/− mice. Cells were treated with 100 nM insulin for 15 min. Representative data from at least three independent experiments are shown. D) Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments showing effects of TCF7L2 depletion on endogenous CREB, CRTC2, or FoxO1 occupancy over G6Pase and PEPCK promoters in primary hepatocytes from TCF7L2 +/+ or TCF7L2 +/− mice. Antibodies against each protein were utilized to detect the association of endogenous transcription factors with the chromatin. Data are shown as the relative enrichment of IP/input ratios of each antibody over that of IgG control. Representative data from at least three independent experiments are shown. Data in A), and D) represent mean ± SD, and data in B) represent mean ± SEM (*;P<0.05, **;P<0.005, ***;P<0.0005, t-test).