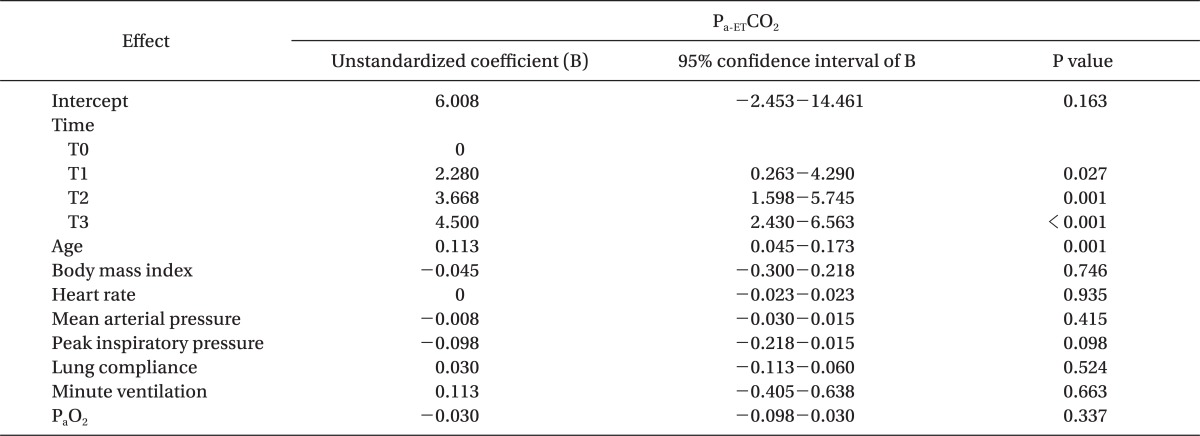
Table 4.
Factors Associated with the Arterial to End-tidal Carbon Dioxide Pressure Gradient (Pa-ETCO2)
The relationships and interactions between Pa-ETCO2 and patient or anesthetic factors (age, body mass index, heart rate, mean arterial pressure, peak inspiratory pressure, minute ventilation, and PaO2) with time were tested using a linear mixed model with adjustment for heart rate, mean arterial pressure, peak inspiratory pressure, minute ventilation, and PaO2. Pa-ETCO2 was significantly related to patient age and duration of pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position, but age was not significantly related to duration of pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position (P = 0.090). T0: 10 min after intubation in the supine position without pneumoperitoneum, T1: 10 min after pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position, T2: 60 min after pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position, T3: 120 min after pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position. PaO2 arterial oxygen partial pressure.