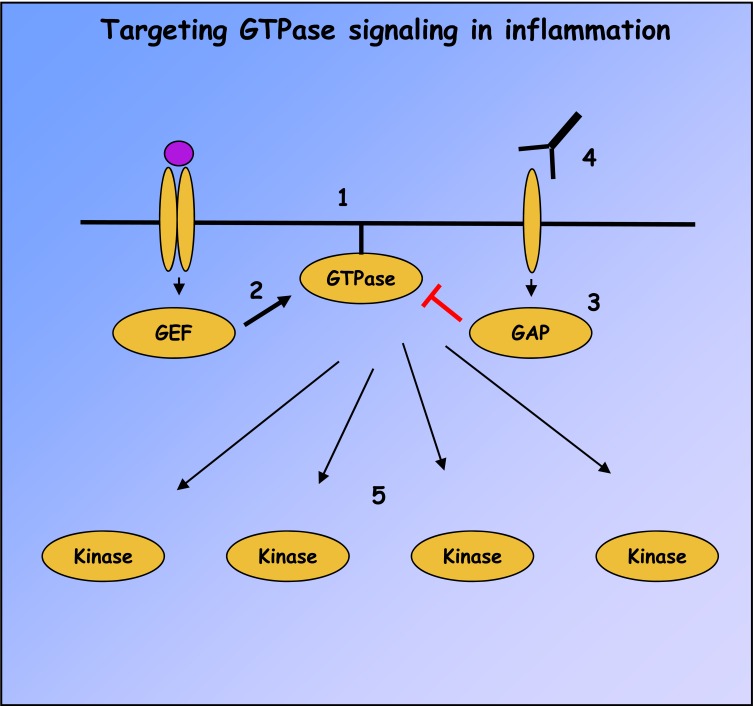
Fig. (3).
Strategies for targeting small GTPase signaling in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Ras superfamily GTPase signaling can be abolished with compounds such as FTIs, geranylgeranyl transferase inhibitors and inhibitory peptides which prevent GTPase membrane localization (1). GTPase activation can also be modulated by small molecular weight compounds targeting GEF catalytic activity or interactions with GTPases, of which activators of EPAC and inhibitors of DOCK2 and Trio are the first examples (2). Similar compounds have not yet been developed to target GAP catalytic activity (3), but receptor antagonists may be identified which can indirectly modulate GAP activity, as in the case of CTLA4-Ig and RapGAP (4). Finally, many downstream effectors of GTPases, like MAP kinases and PI3-Ks, possess catalytic activity and represent pharmacological targets (5).