Figure 12.
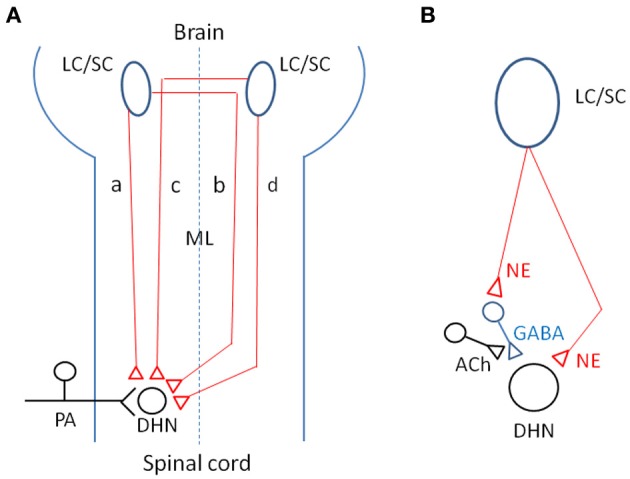
(A) Schematic representation of four CSIPs demonstrated. (a) In ipsilaterally projecting neurons, axons descend the ipsilateral dorsolateral funiculus or ventrolateral funiculus to terminate in the dorsal horn on the side of the descending projection. (b) In ipsilaterally projecting neurons, axons cross the midline within the brain, travel through the contralateral ventrolateral funiculus and recross the midline at spinal segmental levels. (c) In contralaterally projecting neurons, axons cross the midline within the brain and travel through the dorsolateral funiculus to terminate in the dorsal horn on the side of the descending projection. (d) In contralaterally projecting neurons, axons descend through the ipsilateral ventrolateral funiculus and cross the midline at spinal segmental levels. (B) Possible neurotransmitters related to coeruleospinal inhibition of nociceptive signals in the dorsal horn (see text in detail). Keys for the brain and spinal cord are indicated by abbreviations: LC/SC, locus coeruleus/subcoeruleus; ML, midline; PA, primary afferents; DHN, dorsal horn neuron; NE, norepinephrine; ACh, acetylcholine; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid.
