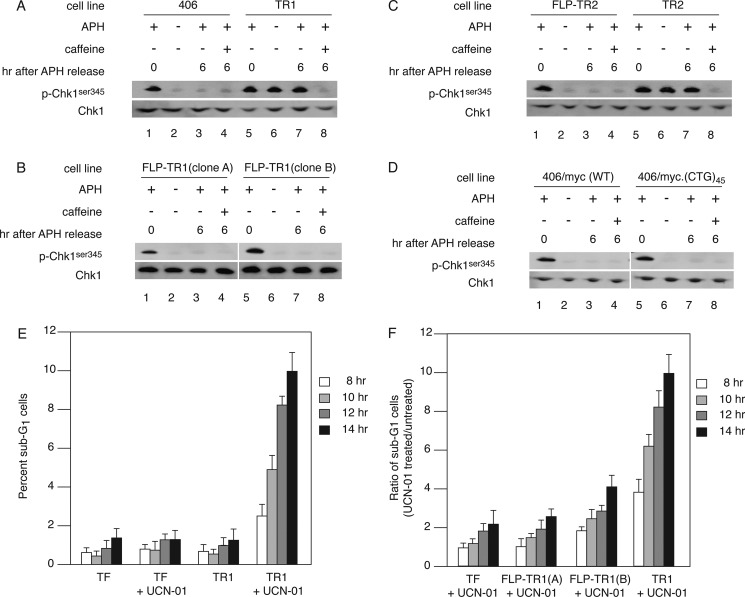
FIGURE 7.
Effects of excision of the c-myc:Pu-Py cassette. A, Chk1 phosphorylation was compared in 406 acceptor cells and TR cells. p-Chk1ser345, phospho-Chk1Ser-345. B, TR1 cells were transfected with plasmid pOG44 encoding the S. cerevisiae FLP recombinase, and clonal cell lines from which the c-myc:Pu-Py cassette had been excised (FLP-TR1(clone A) and FLP-TR1(clone B)) were isolated by limiting dilution. Whole cell lysates were analyzed at the indicated times after aphidicolin treatment, without or with additional caffeine treatment, using anti-Chk1 or anti-phospho-Chk1Ser-345 antibodies. C, the c-myc:Pu-Py cassette was excised by FLP recombinase from an independent line of TR cells (TR2), and Chk1 phosphorylation levels were compared. D, phospho-Chk1Ser-345 are not elevated in cells containing the ectopic wild type c-myc replicator or the wild type c-myc replicator flanked by the (CTG)45-(CAG)45 hairpin-forming sequence (67). E, cells were synchronized with aphidicolin and released into normal medium or medium containing UCN-01 for 8, 10, 12, or 14 h before preparation for flow cytometry. The percentage of sub-G1 cells in each sample at the release times indicated was plotted. Results are from four independent experiments. F, FLP-TR cells are less sensitive to UCN-01 treatment than TR cells. Cells were synchronized with aphidicolin and released into normal medium or medium containing UCN-01 for the indicated times. Plotted is the number of sub-G1 cells in the sample released into UCN-01 divided by the number of sub-G1 cells in a sister culture released into normal medium for the same amount of time. Data shown are representative of at least three experiments per cell line. Error bars in panels E and F indicate S.D.