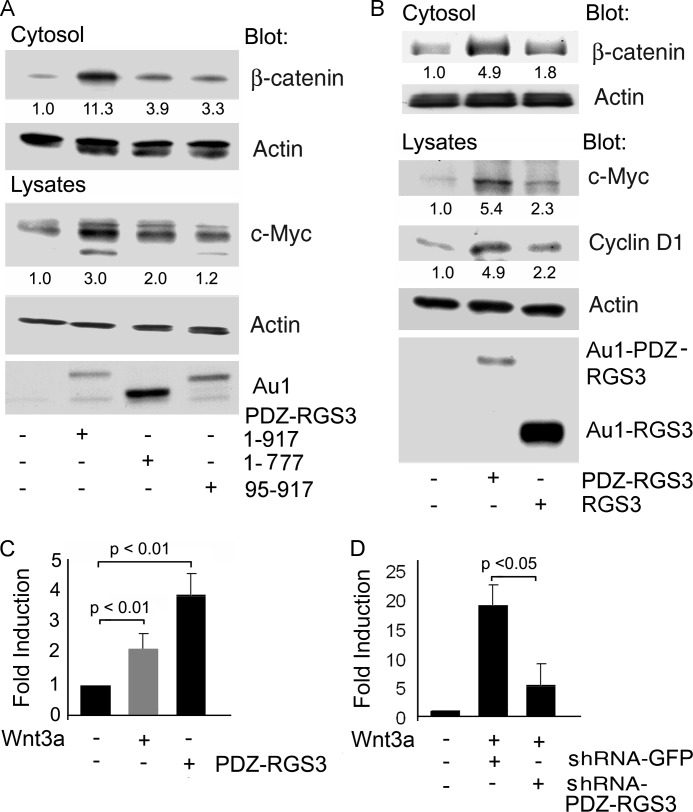
FIGURE 2.
PDZ-RGS3, but not RGS3, enhanced canonical Wnt signaling. A, PDZ and RGS domains of PDZ-RGS3 were needed to increase cytosolic β-catenin levels and facilitate expression of c-Myc. HEK 293 cells were transfected with full-length PDZ-RGS3, RGS-deleted (1–777) or PDZ-deleted (95–917) domain truncated constructs for 24 h. The cells were separated, one half for the cytosolic fraction and the other half for total cell lysates. The levels of cytosolic β-catenin, c-Myc, PDZ-RGS3, and actin were immunoblotted. B, PDZ-RGS3, but not RGS3, induced expressions of c-Myc and cyclin D1. PDZ-RGS3 or RGS3 was transfected into HEK 293 cells. The indicated proteins from the total cell lysates were detected by immunoblotting. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. C, Wnt3a stimulation increased PDZ-RGS3 expression, and PDZ-RGS3 increased c-Myc. RNA extracted from either Wnt3a- or PDZ-RGS3-transfected HEK 293 cells was analyzed by quantitative PCR for PDZ-RGS3 (gray) or c-Myc (black). Results are -fold increase compared with nonstimulated controls following normalization to GAPDH expression and from three separate experiments. D, Wnt3a-stimulated increase in c-Myc expression was inhibited by a PDZ-RGS3 shRNA. RNA extracted from Wnt3a and either control or PDZ-RGS3 shRNA-transfected HEK 293 cells was analyzed by quantitative PCR for c-Myc. Results are -fold increase compared with nonstimulated controls following normalization to GAPDH expression and from three separate experiments.