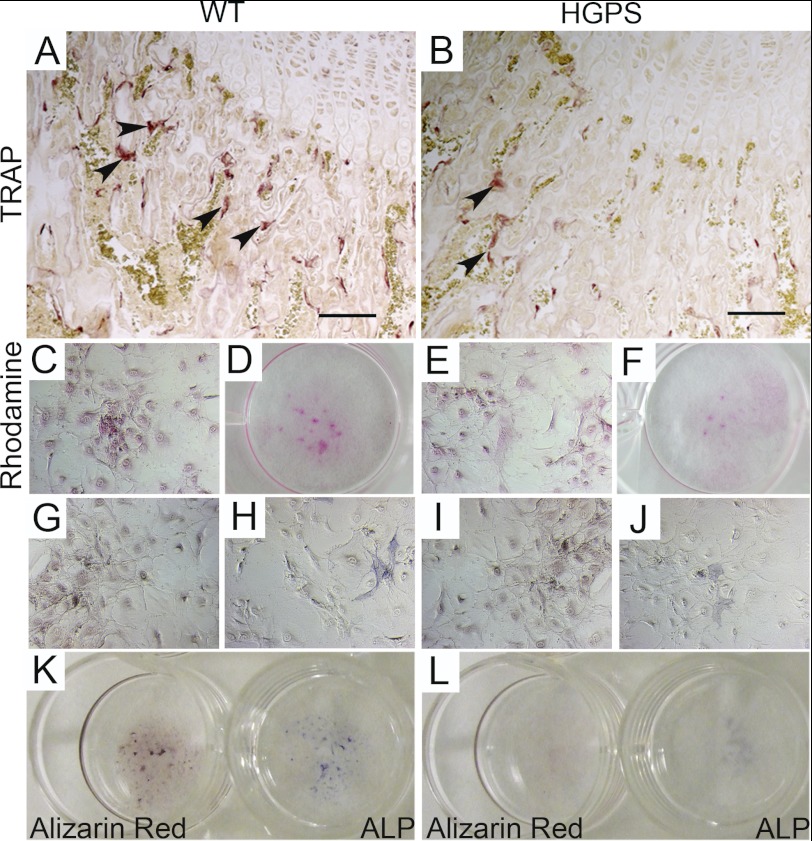
FIGURE 5.
Expression of the HGPS mutation causes a disturbed bone microenvironment and defects in bone matrix deposition. Lower TRAP secretion, detected by enzymatic reaction for acid tartrate phosphatate on femur sections (arrowheads), indicates reduced osteoclast resorption activity in HGPS mice (B). Mineralization assay was performed on primary osteoblast cultures extracted from postnatal day 5-old-mice (C–J) and 12-week-old mice (K and L). Rhodamine B staining was used to check for equal cell number comparing wild-type (C–D) and HGPS mice (E–F). In osteoblast cultures, bone nodule formation was visualized by Alizarin Red staining (G and I) and osteoblastic differentiation by alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining (H and J). Reduced ALP activity and bone nodule formation in primary osteoblast explant cultures was only detected in HGPS mice (L) when compared with wild-type mice (K) isolated from animals at the age of 12 weeks. Scale bars: 50 μm.