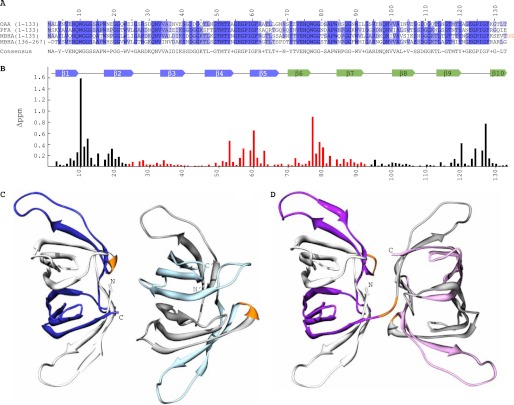
FIGURE 1.
Sequence, carbohydrate binding, and structures of OAAHs. A, amino acid sequence alignment of OAA, PFA, and MBHA. The four sequence repeats in MBHA are displayed as two separate two-sequence stretches. Conserved and similar residues are colored in blue and slate, respectively. The two-residue linker connecting the two domains of MBHA is colored in orange. B, secondary structure and chemical shift perturbation profile (combined amide chemical shift changes) of OAA at the final titration point (1:3 molar ratio of OAA to α3,α6-mannopentaose). Values were calculated using the equation: Δppm = ((Δppm (1HN))2 + (Δppm (15N)/5)2)1/2. C and D, ribbon representation of the backbone structures of PFA and MBHA, respectively. The five β-strands in the first and second sequence repeats in PFA are colored in white and blue and in gray and light blue for molecule one and two, respectively, in the asymmetric unit. For MBHA, the five β-strands in the first and second sequence repeats in the first and second domains are colored in white and purple and in gray and light magenta, respectively. The connecting residues between the repeats (between strands β5 and β6) in both proteins and between the first and second domains in MBHA are colored in orange.