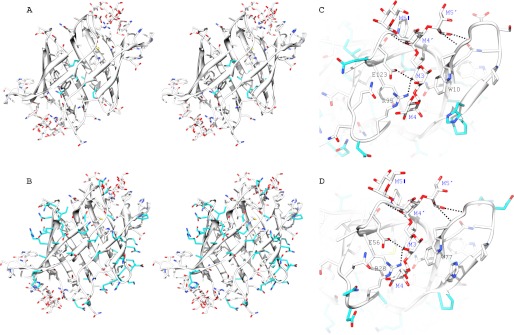
FIGURE 6.
Structural model of α3,α6-mannopentaose-bound PFA based on the OAA-α3,α6-mannopentaose complex. A and B, stereo views of the PFA carbohydrate binding sites 1 and 2, highlighting amino acid differences between OAA and PFA in the hydrophobic (A) and solvent-exposed regions (B). C and D, predicted intermolecular hydrogen bonds between PFA and α3,α6-mannopentaose (black dashed lines) in binding sites 1 (C) and 2 (D). Residues that are in direct contact with the carbohydrate are identical in PFA and OAA: Trp10, Gly11, Gly12, Arg95, Glu123, and Gly124 in binding site 1 (C) and Trp77, Gly78, Gly79, Arg28, Glu56, and Gly57 in binding site 2 (D). The protein is depicted in both ribbon and stick representation, with bound α3,α6-mannopentaose in stick representation only. All carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms of the conserved residues in PFA and OAA and in the carbohydrates are shown in white, red, and blue, respectively. The carbon atoms of differing residues in PFA and OAA are colored in cyan. Amino acids are labeled by single-letter code, and the sugar rings of the carbohydrate are labeled according to standard nomenclature.