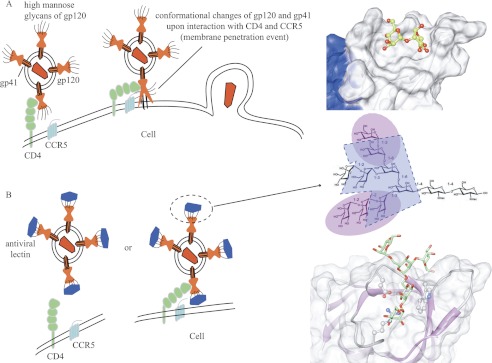
FIGURE 9.
Schematic depiction of HIV inactivation by Cyanovirin-N homolog (CVNH) and OAAH lectins. A, in the absence of antiviral lectins, the interaction between gp120 and CD4 introduces a conformational change that allows the fusion peptide of gp41 to penetrate the cell membrane, leading to viral-cell membrane fusion and HIV capsid deposition into the cell. B, in the presence of antiviral lectins, they bind to the high mannose glycans on gp120/41, preventing the required conformational change, thereby blocking infection. The glycan epitopes of Man-9 that are recognized by CV-N (highlighted in magenta) and OAA (highlighted in blue) as well as their detailed interactions at the atomic level are provided at the right-hand side.