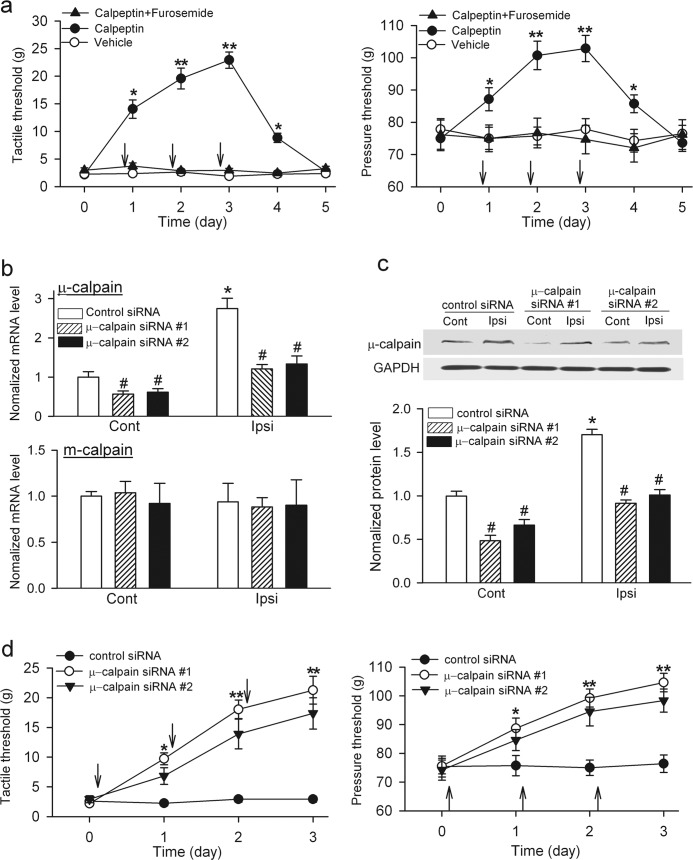
FIGURE 7.
Inhibition of calpain or knockdown of μ-calpain at the spinal level reduces SNL-induced pain hypersensitivity. a, shown are mean effects of intrathecal administration of calpeptin (100 μg, twice a day for 3 consecutive days, n = 10 rats), vehicle (1% DMSO, n = 7 rats), or calpeptin plus furosemide (100 μg twice a day for 3 consecutive days, n = 7 rats) on the withdrawal thresholds in response to von Frey filaments (left) or noxious pressure (right) applied to the left hind paw of rats 4 weeks after SNL. Each measurement was conducted 2 h after intrathecal injection (indicated by arrows). b, shown is quantification of the mRNA levels of μ-calpain (top) and m-calpain (bottom) in the dorsal spinal cord ipsilateral (Ipsi) and contralateral (Cont) to SNL in rats treated with control siRNA or two different μ-calpain-specific siRNA for 3 days (n = 6 in each group). c, shown are Western blots and quantification of μ-calpain proteins in the dorsal spinal cord ipsilateral (Ipsi) and contralateral (Cont) to SNL in rats treated with control siRNA or two different μ-calpain-specific siRNA for 3 days (n = 6 in each group). d, shown are the mean effects of intrathecal administration of scrambled control siRNA (n = 8 rats) and two different μ-calpain-specific siRNA (5 μg, once a day for 3 consecutive days; #1 sRNA, n = 9 rats; #2 sRNA, n = 7 rats) on the withdrawal thresholds in response to von Frey filaments (left) or noxious pressure (right) applied to the left hind paw of rats 4 weeks after SNL. Measurements were performed before siRNA injection each day (indicated by arrows). #, p < 0.05 compared with the control siRNA group; * p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, compared with the baseline or contralateral side, one-way analysis of variance test. Error bars represent S.E.