Fig. 7.
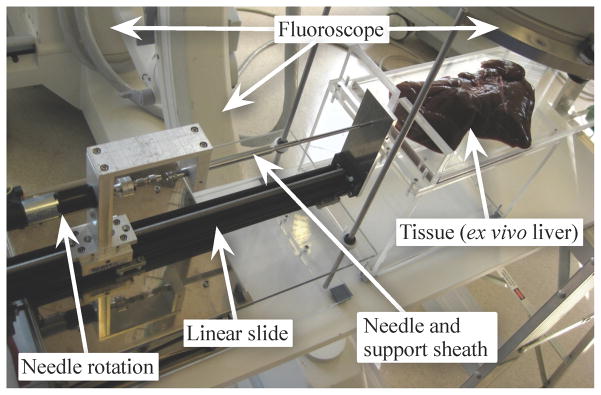
Our portable needle steering device is designed to fit under a fluoroscope while allowing control of the needle’s insertion and rotation. When using conventional fluoroscopy, only one image plane is available, so the planar controller is unable to determine the height of the needle. Our experimental validation used a similar device that uses two cameras to triangulate the needle tip inside a transparent artificial tissue. Clinical procedures will use bi-plane fluoroscopy or 3D ultrasound to directly measure the needle tip position inside the tissue.