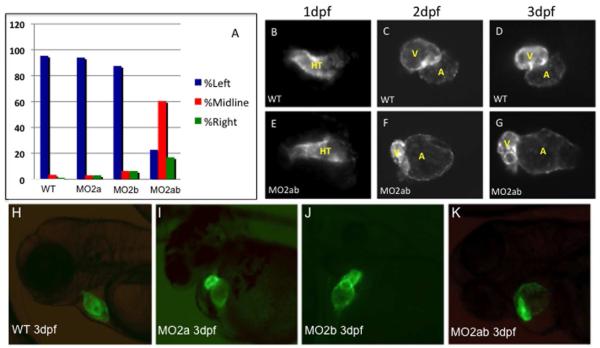
Fig. 4. Chamber morphogenesis is disrupted in the tbx2ab morphants.
(A) Unlike single morphants, the tbx2ab double morphants show a heart tube jogging phenotype at 24 hpf. Wildtype and morphant embryos were evaluated at 24 hpf for the position of the primitive heart tube and scored as jogging left (normal, blue bars, right (green bars), or remaining midline (red bars). The Y axis indicates percentage of wildtype (WT), tbx2a morphant (MO2a), tbx2b morphant, or tbx2ab double morphant embryos. For each sample n = 50. (B-G) Cardiac morphogenesis is visualized by imaging expression of the myl7:gfp transgenic reporter gene in wildtype (WT, top panels) or tbx2ab morphants (MO2ab, lower panels), at 1 dpf (B, E), 2 dpf (C, F) or 3 dpf (D, G). HT indicates the heart tube, while V marks the ventricle and A marks the atrium. Note that the heart tube shape is relatively normal at 1 dpf but is markedly altered in chamber morphology by 2 or 3 dpf. Each panel shows the heart of a representative embryo. For each sample, n>100. The large atrium, small ventricle phenotype was scored in 110/172 tbx2ab morphants (64%). (H-K). The tbx2ab double morphants have distinct alterations in chamber morphology. Shown are representative wildtype (A), tbx2a morphant (B), tbx2b morphant (C), or tbx2ab double morphant (D) embryos at 3 dpf in the myl7:gfp background. While hearts of the single morphants do not loop properly, due to emerging defects in AVC development at this stage, the chamber sizes, although variation was noted, are similar to those of wildtype embryos. In contrast, chamber sizes in the double morphant are significantly disturbed. Over 100 embryos were analyzed for each, taken from multiple independent experiments.