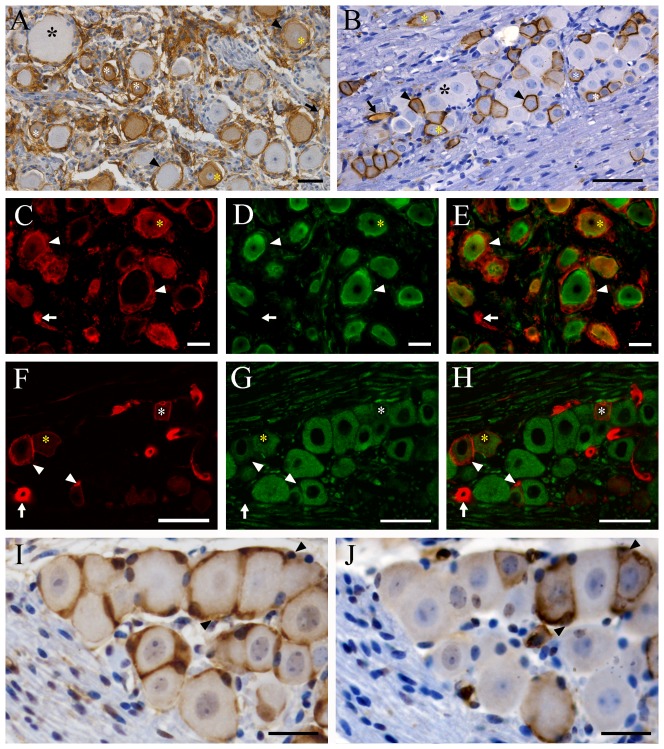
Figure 1. Localization of AQP1 in the trigeminal ganglion of humans (A, C–E) and mice (B, F–H).
(A–B) Representative images of immunohistochemistry for AQP1. (C–H) Representative images of double immunofluorescence with AQP1 (red) and β-tubulin III (green). Some small-sized (white asterisks) and medium-sized (yellow asterisks) trigeminal neurons of humans and mice are positive for AQP1 which is localized to the cell membrane and cytoplasm. Large-sized trigeminal neurons (black asterisks) of the two species are negative for AQP1. Satellite cells expressing AQP1 (arrowheads) are observed around both AQP1-negative and -positive trigeminal neurons in humans, but only around AQP1-positive trigeminal neurons in mice. Both human and mouse capillary endothelial cells (arrows) express AQP1. (I–J) Immunolocalization of glutamine synthetase (I) and AQP1 (J) in the 10 µm adjacent sections of mouse trigeminal ganglion. Each neuron is wrapped tightly by GS-positive satellite glial cells (arrowheads in I). However, AQP1 immunoreaction (arrowheads in J) is only localized to satellite cells surrounding AQP1-positive trigeminal neurons. Scale bars = 50 µm in A–H; 15 µm in I and J.