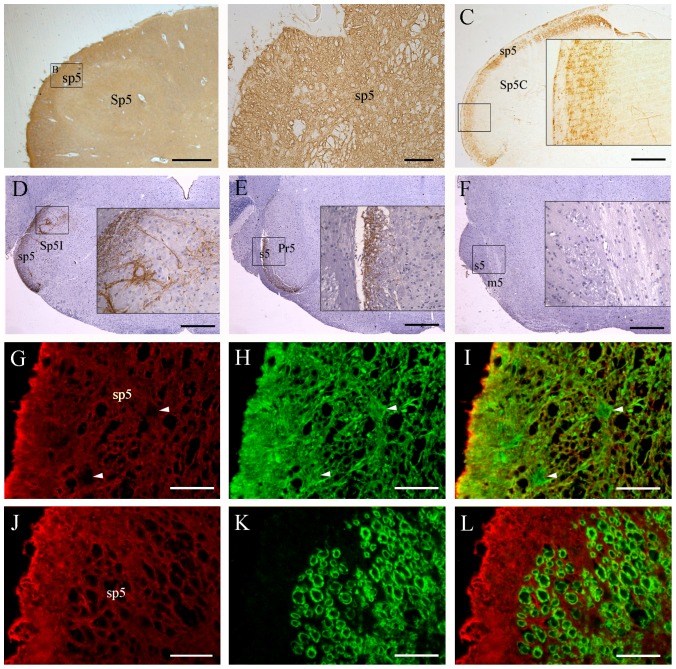
Figure 4. Localization of AQP1 in the brain stem of humans (A, B, G–L) and mice (C–F).
(A–F) Representative images of immunohistochemistry for AQP1. (G–L) Representative images of double immunofluorescence of AQP1 (red) with GFAP (green in H) or β-tubulin III (green in K) in the sp5. There is extensive expression of AQP1 throughout the human medulla oblongata including the spinal trigeminal tract (sp5) and spinal trigeminal nucleus (Sp5, A and B). AQP1 and GFAP are highly colocalized at the glial lamellae along the medulla surface as well as astrocyte processes within the brain parenchyma (G–I). Interestingly, astrocyte cell bodies (arrowheads in I) do not express AQP1. No β-tubulin III positive axons coexpress AQP1 in the sp5 (L). In the mouse brain stem, dense dot-like AQP1 labeled nerve fibers are present in the caudal part of sensory root of the trigeminal nerve (s5, E) and sp5 (C and D), but not at the rostral part of s5 or at the motor root of the trigeminal nerve (m5, F). Moreover, AQP1 positive axonal terminals are observed in the caudal and interpolar parts of the trigeminal nucleus (Sp5C and Sp5I, C and D), but not in the principal sensory trigeminal nucleus (Pr5, E). Scale bars = 1 mm in A; 200 µm in B, G–L; 400 µm in C–F.