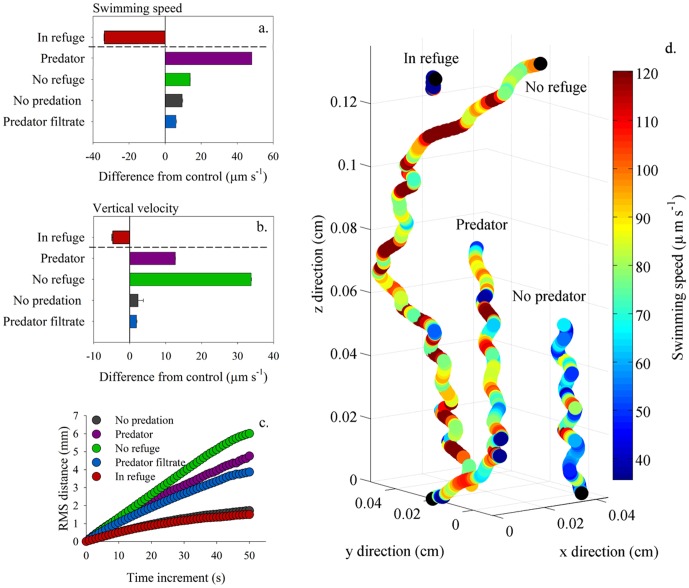
Figure 4. Impact of predator-derived stimuli on movement behaviors.
Modulation of phytoplankton movements as a function of predator-derived cues. Difference in (a) swimming speed (µm s−1) and (b) vertical velocity (µm s−1), above and below the halocline (dotted line), (c) root mean square distance (mm), a proxy of population dispersal rates and (d) characteristic swimming tracks and speeds in the different predator exposure treatments; black circles denote the beginning of a swimming track. Fleeing behavior by the phytoplankton was significant but quantitatively different in response to specific predator-derived cues as evident in swimming metrics, tracks, and dispersal.