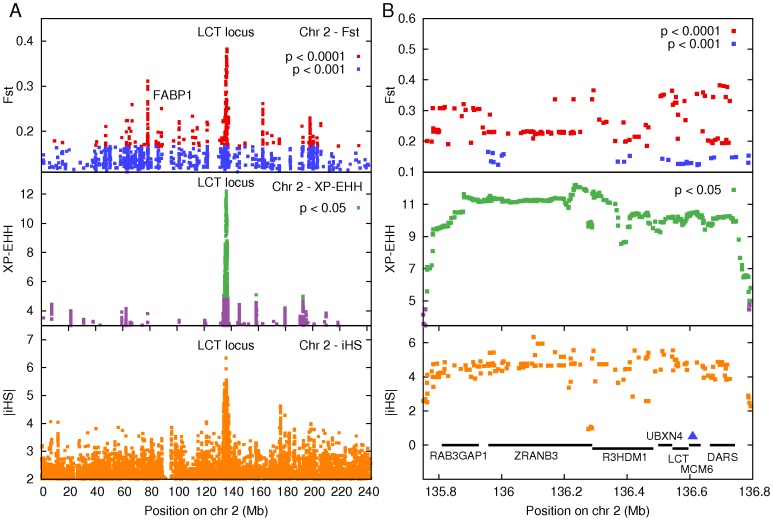
Figure 2. (a) Genome-wide significant scores identifying candidate regions under selection on Chromosome 2.
Chromosome wide plot of SNPs with significant scores using Fst (empirical p-value <0.001 and Bonferroni corrected permutation test pB <8.6E−6), iHS (normalized |iHS|>2), and XP-EHH (XP-EHH ≥4.796, two-tailed Bonferroni corrected p≤0.05). The SNPs thus identified were clustered on the basis of linkage disequilibrium to identify contiguous genomic regions that are candidates for selections (Table 1,2,3,4). The locus containing the genes LCT and MCM6 (135–137 Mb) was identified by all three metrics as the top candidate for selection. The non-synonymous TC polymorphism at rs2241883 in the FABP1 gene had most significant genome-wide Fst (Fst = 0.25, pE = 3.13E−5). The MKK samples have a high frequency (∼0.45) of the protective C allele, known to be associated with low cholesterol levels in Europeans (plots for other chromosomes in Appendix S6). (b) Inset of the LCT locus on Chromosome 2.An inset of the Fst, iHS and XP-EHH scores for SNPs in the ∼ 1 Mb locus (from 135.8–136.8 Mb) on Chr 2 containing the genes LCT and MCM6. The uniformly high values for all three metrics in this region suggest that this locus has undergone strong selection pressure. The blue marker indicates the position of the lactase associated SNP in MCM6 that we sequenced, which was polymorphic in MKK with frequency pC = 0.58+/−0.14 (68% CI) for the protective C allele.