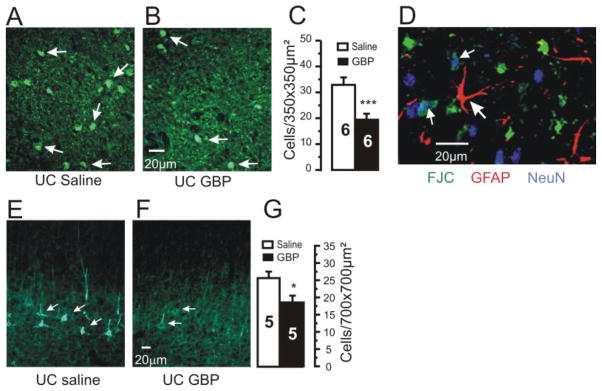
Figure 2. Neuroprotective effects of chronic GBP treatment.
A–B: Representative confocal images of Fluoro-Jade C (FJC) staining from UC cortices of rats treated for 2d with saline (A) or GBP (B). Sections obtained 7 days after cortical injury. Arrows: FJC positive profiles.
C: Density of FJC positive cells/350×350 μm2 in layer V of UC cortex is decreased by GBP treatment. Graph shows data from 6 saline- and 6 GBP-treated UC rats. Counts done from 6–9 images and 2–3 sections/rat. ***P < 0.001. Error bars: SEM.
D: FJC positive profiles were neuronal. Confocal image from section triple labeled for FJC (green), GFAP-IR (red) and NeuN (blue). FJC did not colocalize with GFAP (large arrow), however a number of profiles were reactive for NeuN and FJC (small arrows). Calibration bar in B for A,B and in F for E,F.
E–F: 200KDa neurofilament-IR sections through UC from rat treated with saline (E) and GBP (F).
G: Graph shows significant decrease in density of neurofilament IR (#cells/700×700 μm2) in GBP-treated rats. Numbers in columns: # rats. *: p<0.05