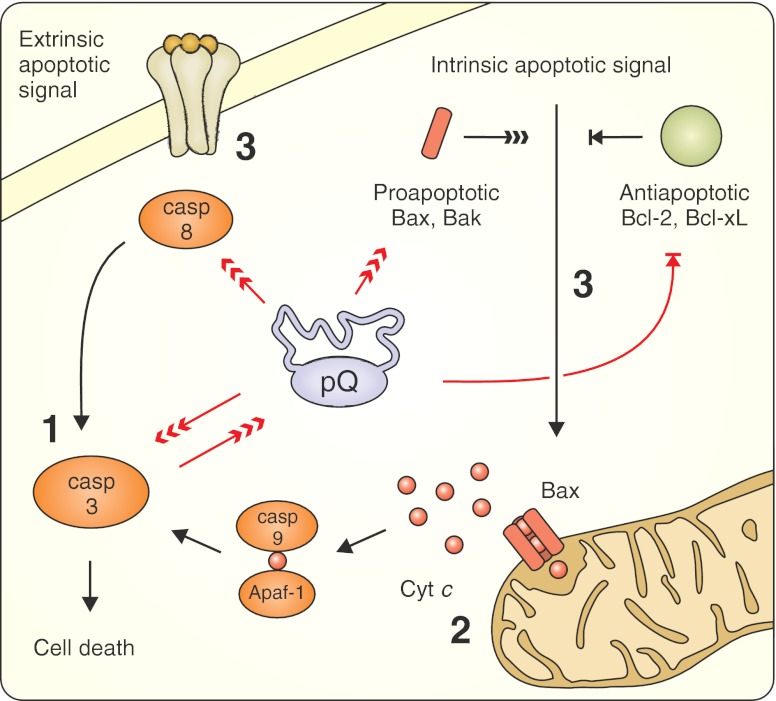
Fig. 6.
Anti-apoptotic therapeutic strategies target aberrant interactions between polyglutamine proteins and the components of apoptotic pathways. PolyQ proteins cause the upregulation and/or activation of several caspases, upregulate pro-apoptotic proteins and downregulate anti-apoptotic factors, which may subsequently lead to the release of apoptogenic proteins from mitochondria. Several polyQ proteins undergo proteolytic cleavage by caspases, which results in the production of toxic truncated protein fragments. Therapeutic approaches tested in mouse models include the inhibition of caspase functions (1), the inhibition of mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and subsequent intrinsic apoptotic pathway activation (2), and the modulation of the initiation of apoptotic signals (3). Cytochrome c (Cyt c), apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1)