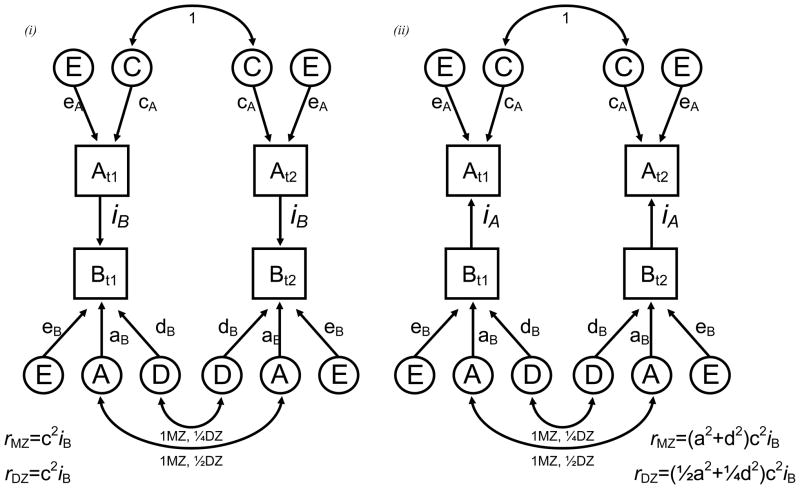
Figure 1.
Uni-directional causal modeling between two variables with the expected cross-twin cross-trait correlations for monozygotic (rmz) and dizygotic (rdz) twin pairs (t1 & t2) under the (i) A causes B and (ii) B causes A hypotheses.
A, C, E and D refer to additive genetic, shared environment, non-shared environment and genetic dominance respectively.
Double headed arrows illustrate the expected twin pair (cross-twin) correlations. DZ twin pairs share on average half of the DNA so the expected twin pair correlations are ½ and ¼ for additive genetic and dominance effects respectively. Expected cross-twin cross-trait correlations are derived using Wright’s (1934) path tracing rules.