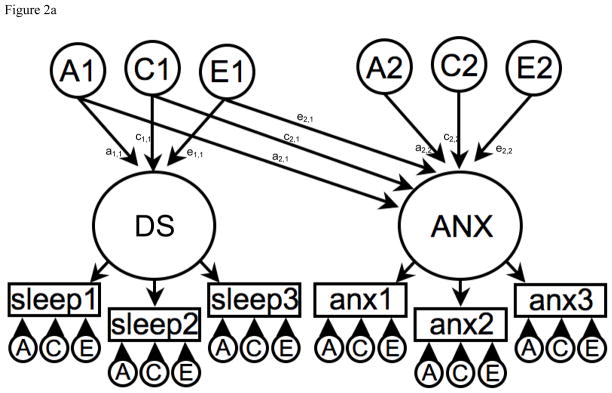
Figure 2.
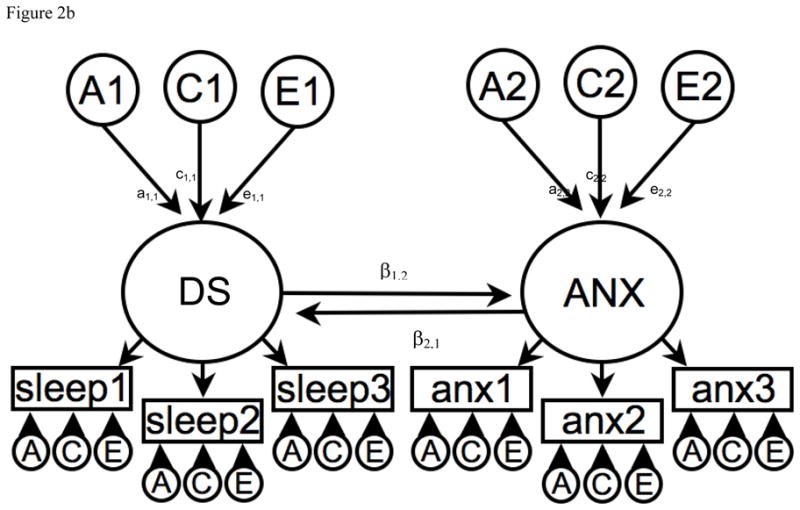
Figure 2a. Correlated liabilities model to explain the phenotypic association between Disrupted Sleep (DS) and Anxiety (ANX).
A1, C1 & E1 = latent additive genetic shared and non-shared environmental risks for Disrupted Sleep (DS).
A2, C2 & E2 = latent additive genetic shared and non-shared environmental risks for Anxiety (ANX).
DS and ANX are common factors indicated by observed phenotypic symptoms for sleep 1–3 and anx 1–3 respectively which have their own item specific latent genetic and environmental risk factors.
The non-causal association is represented by the pathway coefficients between the DS and ANX common factors i.e. via a1,1a2,1, c1,1c2,1 and e1,1e2,1.
Figure 2b. Reciprocal interaction model to explain the phenotypic association between Disrupted Sleep (DS) and Anxiety (ANX).
A1, C1 & E1 = latent additive genetic shared and non-shared environmental risks for Disrupted Sleep (DS).
A2, C2 & E2 = latent additive genetic shared and non-shared environmental risks for Anxiety (ANX).
DS and ANX are common factors indicated by observed phenotypic symptoms for sleep 1–3 and anx 1–3 respectively which have their own item specific latent genetic and environmental risk factors.
The causal association is represented between the DS and ANX common factors i.e. β1,2 from DS to ANX and β2,1 from ANX to DS.