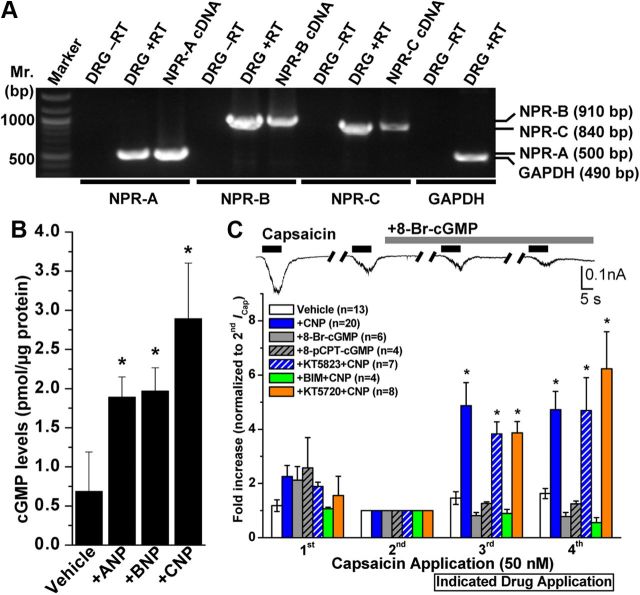
Figure 2.
Expression of NP receptors and role of downstream cGMP signaling in mouse DRG neurons underlying CNP modulation of TRPV1 channel activity. A, All three NP receptors (NPR-A, NPR-B, and NPR-C) are expressed in DRG neurons. Representative RT-PCR analysis of NPR expression in cultured mouse DRG neurons with primers specific for NPR-A, NPR-B, and NPR-C, as well as for GAPDH as the housekeeping gene. B, ELISA-based quantification of intracellular cGMP levels in isolated mouse DRG neurons after ANP, BNP, or CNP treatment (100 nm for 30 min). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05, significantly different compared with the vehicle group (Student's t test). C, CNP-induced sensitization of TRPV1 is dependent on PKC, but not cGMP–PKG or PKA, signaling. Top panel shows representative traces of TRPV1 currents in small/medium-diameter cultured mouse DRG neurons in response to four successive applications of capsaicin (50 nm for 5 s; with 1 min interval), with continuous extracellular perfusion of 8-Br-cGMP (100 μm) after the second Icap. Bottom panel shows the quantification of ICap with indicated drug treatments [100 μm 8-Br-cGMP, 200 μm 8-pCPT-cGMP, 10 nm CNP, 10 nm CNP + 500 nm KT5823 (PKG inhibitor), 10 nm CNP + 400 nm KT5720 (PKA inhibitor), and 10 nm CNP + 1 μm BIM (PKC inhibitor)]. Peak ICap amplitudes are normalized to second ICap application of the respective vehicle or treatment groups, and the data are presented as mean ± SEM of fold-increase in ICap compared with second ICap (respective n values are shown in the figure). *p < 0.05, significantly different compared with the vehicle group (one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett's correction).