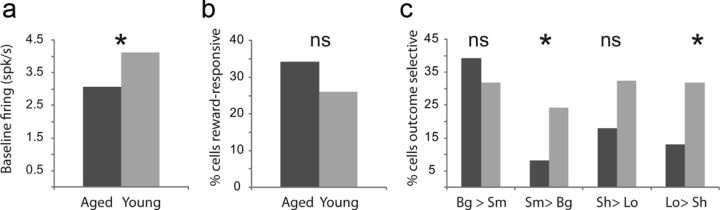
Figure 2.
Outcome selectivity in ABL is reduced in aged animals. a, Baseline firing as computed during 1 s before nose poke. Baseline firing was reduced in aged ABL (t test; p < 0.05). b, The number of reward-responsive neurons in ABL (higher firing 1 s after reward compared with baseline; t test; p < 0.05) was not significantly different between aged and young rats (χ2 = 3.7; p = 0.05). c, Height of each bar indicates the percentage of neurons that showed a significant effect of delay or size in an ANOVA during the 1 s after reward delivery (p < 0.05). Asterisks reflect significant difference between counts of neurons in each group as measured by χ2 (p < 0.05).