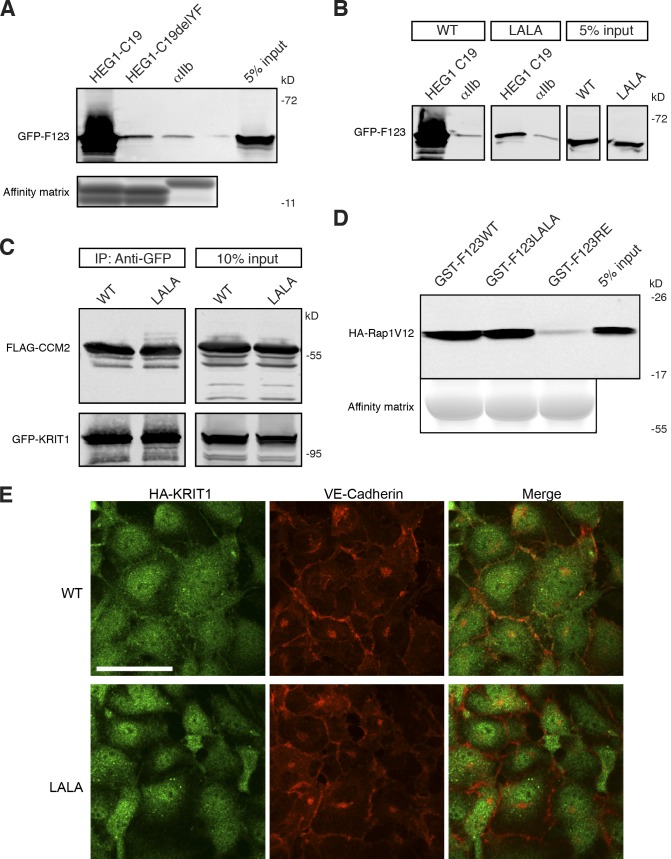
Figure 4.
Reduced binding of KRIT1 (L717,721A) to HEG1. (A) HEG1 C19 cytoplasmic tail model protein binds to recombinant GFP-KRIT1 FERM from HEK293 cell lysates. HEG1 C19delYF, which lacks the last two residues, does not bind to GFP-KRIT1 FERM. (bottom) The equal loading of tail proteins as judged by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. Blots are representative of three experiments. (B) HEG1 C19 tail model protein binds to recombinant GFP-KRIT1 FERM from HEK293 cell lysates but not GFP-KRIT1 FERM(L717,L721A). Both WT and mutant proteins are expressed at similar levels. All lanes were from the same gel. (C) Both GFP-fused KRIT1 WT and GFP-fused KRIT1(L717,721A) are associated with CCM2 at equivalent levels as assessed by coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. All lanes were from the same gel. (D) Both GST-KRIT1 F123 and GST-KRIT1 F123(L717,721A) bind to HA-Rap1V12 from HEK293 cell lysates. GST-KRIT1 F123(R452E) mutant serves as a negative control as it does not bind to Rap1. (E) HA-tagged KRIT1 WT colocalizes with VE-cadherin at HUVEC cell–cell junctions. In contrast, HA-KRIT1(L717,L721A) does not . HA-KRIT1, green. VE-cadherin, red. IP, immunoprecipitation; LALA, KRIT1(L717A,L721A). Bar, 50 µm.